Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare kind of cancer, occurs in different tissues or organs. It commonly happens in salivary glands, and also exists in breast, lung, brain and the paranasal sinuses. The disease causes a lot of death all around the world.
p53 (Tumor protein p53) is a crucial tumor suppressor, prevents cancer formation. It regulates the cell cycle, apoptosis, and genomic stability. Normally, p53 remains inactivated due to its negative regulator, MDM2. Once DNA damage and other stresses happen, the p53-MDM2 complex will dissociate. Then, p53 turns to an active form and causes either DNA repair or cell apoptosis. Thus, inhibition of MDM2 to activate p53 becomes a promising way in cancer therapy.
MI-773 is a potent MDM2 inhibitor, binds to MDM2 with high affinity (Ki, 0.88 nM). It blocks p53-MDM2 interaction, inhibits p53 protein degradation mediated by MDM2, and leads to p53 accumulation. The inhibitor also activates downstream transcription of p53 targeted genes.
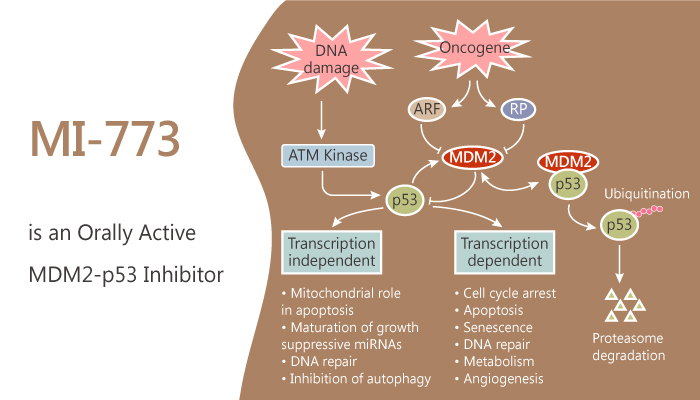
In addition to the effect on MDM2 inhibition, MI-773 exhibits excellent activity on ACC regression. In SCID mice bearing patient-derived xenograft (PDX), MI-773 (10 mg/kg) suppresses the rate of tumor growth modestly. It causes significant tumor regression at 100 mg/kg.
Moreover, MI-773 induces apoptosis of tumor cells. It also decreases the population of cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. Totally, MI-773 is a potent and specific pro-apoptotic compound via p53 activation.
References:
1. Warner KA, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;22(14):3550-9.