The Sine oculis homeobox homolog 1 (SIX1)/eyes absent (EYA) transcription complex plays a key role in the development of multiple organs. Specifically, members of the SIX gene family encode proteins characterized by different DNA binding homologous domains and upstream six domains. This may involve determining DNA binding specificity and mediating protein-protein interactions. Besides, the genes in the SIX families play a role in the development of vertebrates and insects. They are related to the maintenance of tissue differentiation.
Moreover, the SIX1 homeobox gene plays a key role in the development of many organs by promoting the proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion of precursor cells. SIX1 is a key regulator of embryonic development. Furthermore, it needs to interact with the EYA protein family (EYA1-4) to activate the transcription of genes involved in neurogenesis, myogenesis, and nephrogenesis. The EYA family members of SIX1 coactivators (EYA1-4) play a key role in SIX1 mediated transcriptional activation. Meanwhile, the interaction of SIX1 and EYA forms the necessary transcription factors for mammalian development. Targeting SIX1- EYA interaction may inhibit breast cancer progression. Here, we will introduce a potent SIX1/EYA2 interaction inhibitor,NCGC00378430.
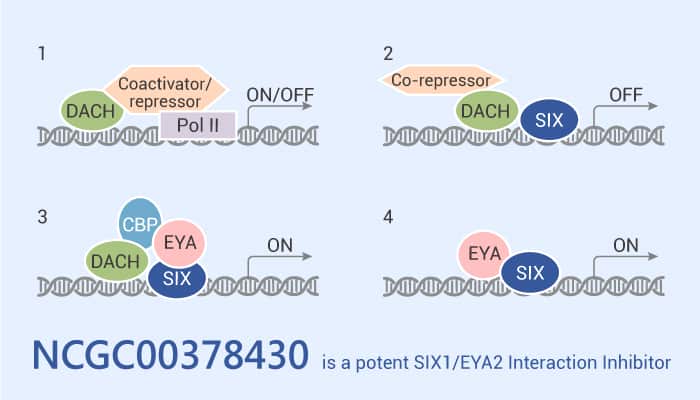
NCGC00378430 is a Potent SIX1/EYA2 Interaction Inhibitor.
First of all, NCGC00378430 is a potent SIX1/EYA2 interaction inhibitor with an IC50 of 52 μM in the Alphascreen assay. Nonetheless, NCGC00378430 partially reverses transcriptional and metabolic profiles mediated by SIX1 overexpression. Interestingly, NCGC00378430 reverses SIX1-induced TGF-β signaling and EMT. NCGC00378430 inhibits SIX1-mediated breast cancer metastasis in a mouse model.
In the second place, NCGC00378430 with 20 μM for 3 days blocks TGF-β induced activation of p-Smad3, upregulation of FN1, and downregulation of E-CAD in T47D cells. Importantly, NCGC00378430 reverses the SIX1-induced increase in p-SMAD3 and does not alter total E-CAD levels. NCGC00378430 restores membranous E-CAD in MCF7-SIX1 cells, along with inhibiting FN1 expression. Particularly, NCGC00378430 disrupts SIX1-EYA2 interaction in breast cancer cells (MCF7, T47D, MDA-MB-231 cells). Obviously, NCGC00378430 partially reverses SIX1-mediated transcriptional and metabolic signatures in MCF7 breast tumor cells.
Last but not the least, NCGC00378430 with 25 mg/kg every other day for 17 days dramatically decreases distant metastatic burden compared to vehicle treatment. Additionally, NCGC00378430 has no growth inhibitory effect. NCGC00378430 with 20 mg/kg by IV has a T1/2α of 0.25 hours.
All in all, NCGC00378430 is a potent SIX1/EYA2 interaction inhibitor.
References:
Hengbo Zhou, et al. Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 15;80(12):2689-2702.