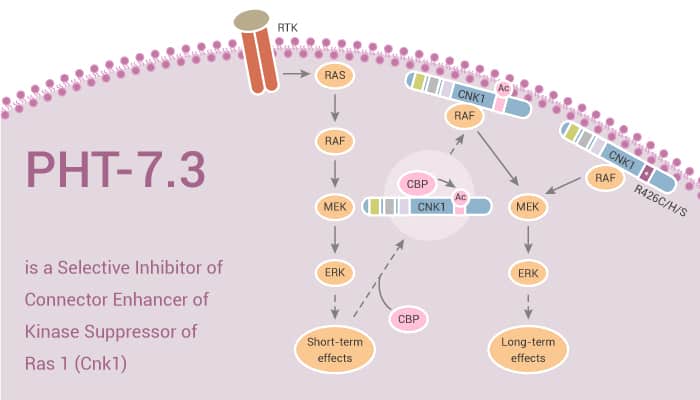
Cnksr1 (Cnk1) is a multidomain scaffold protein important for cell proliferation, survival, and migration. Cnk1 can act as a scaffold for a number of Ras and Rho GTPase family members, while translocating its binding partners to cell membranes where signaling is initiated. Cnk1 is a scaffold for the Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk signaling cascade, possibly as part of a cell membrane Ras signaling nanocluster. Point mutation of the KRAS gene (mut-KRAS) is the most common proto-oncogenic event in human cancer. Approximately 25% of human cancers show the highest levels in pancreatic, colon cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma. Mut-KRas activates downstream signaling that ultimately leads to the mut-KRas phenotype of altered proliferation, anchorage independent growth, invasion, and tumorigenesis. PHT-7.3 bound selectively to the PH domain of Cnk1, preventing plasma membrane colocalization with mut-KRas. It inhibits mut-KRas, but not wild-type KRas cancer cell and tumor growth and signaling.
PHT 7.3 blocks the growth of mutant KRAS cells and tumors.
The Cnk1 PH domain binding compound PHT 7.3 inhibits the proliferation of mut-KRas cells in vitro. PHT-7.3 demonstrated the desirable qualities of binding to the PH domain of Cnk1, selective inhibition of mut-KRas NSCLC cell growth and signaling, good in vivo pharmacokinetic properties. when dosed daily at 200 mg/kg ip for up to 20 days, PHT-7.3 exhibited cytostatic antitumor activity in the mut-KRas(G12S) A549 xenograft and mut-KRasG12V H441 xenograft but not in the wt-KRas H1975 NSCLC xenograft. In addition, in vivo antitumor studies with PHT-7.3, alone and in combination with erlotinib or trametinib, show inhibition of mut-KRas tumor growth but little effect on wt-KRas tumor growth.
PHT-7.3 binds selectively to the PH domain of Cnk1 preventing plasma membrane binding with mut-KRas. It has the ability to inhibit mut-KRas, cancer cell and tumor growth and signaling, but not that of wt-KRas. Thus, the PH domain of Cnk1 is a druggable target whose inhibition selectively blocks mutant KRas activation.
Reference:
Indarte M, et al. Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 15;79(12):3100-3111.