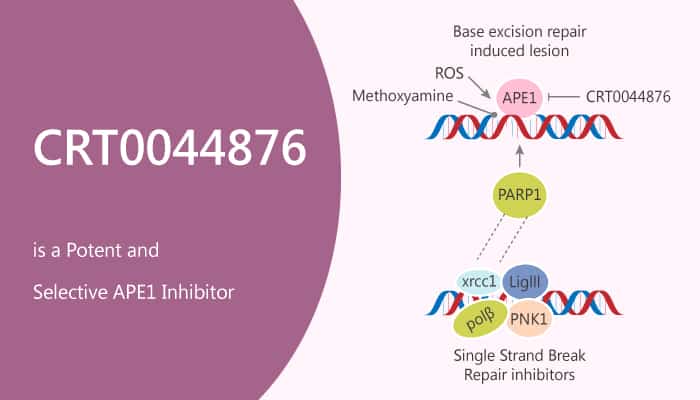
The base excision repair (BER) pathway is essential for the removal of DNA bases damaged by alkylation or oxidation. This pathway also handles a variety of other lesions including deaminated bases and DNA single-strand breaks. A key step in BER is the processing of an apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site intermediate by an AP endonuclease. The major AP endonuclease in human cells (APE1, also termed HAP1 and Ref-1) accounts for >95% of the total AP endonuclease activity and is essential for the protection of cells against the toxic effects of several classes of DNA damaging agents. APE1 performs roles in DNA repair other than AP site processing. APE1 also plays a role in the nucleotide incision pathway. In addition, APE1 overexpression has a relation to radio- and chemo-resistance in human tumors. In this study, CRT0044876 is a potent and selective APE1 inhibitor.
CRT0044876 is a potent and selective APE1 inhibitor.
CRT0044876 has an IC50 for inhibition of APE1 of ∼3 μM and not only inhibits AP site cleavage catalyzed by purified APE1, but also cleavage directed by APE1 in a HeLa whole-cell extract. Moreover, it inhibits the 3′-phosphoglycolate diesterase activity of APE1 with an IC50 of ∼5 μM. CRT0044876 inhibits the AP endonuclease, 3′-phosphodiesterase, and 3′-phosphatase activities of APE1, and is a specific inhibitor of the exonuclease III family of enzymes to which APE1 belongs. Furthermore, it potentiates the cytotoxicity of several DNA base-targeting compounds. In addition, CRT0044876 inhibits both the exonuclease and AP endonuclease activities of exonuclease III, but shows no inhibitory activity towards endonuclease IV. Last, it has minimal effects on BamHI restriction endonuclease or topoisomerase I even at CRT0044876 concentrations of 100 μM.
In summary, CRT0044876 is a potent and selective APE1 inhibitor. At non-cytotoxic concentrations, it potentiates the cytotoxicity of several DNA base-targeting compounds. Thus, CRT0044876 is a novel reagent for probing APE1 function in human cells. It also provides a rational basis for the development of APE1-targeting drugs for antitumor therapy.
Reference:
Madhusudan S, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(15):4711-4724. Published 2005 Aug 19.