Chemoresistance is a major cause of cancer treatment failure. Tumor-initiating cells (TIC) have attracted a considerable amount of attention due to their role in chemoresistance and tumor recurrence. The inhibition of AurA kinase by AKI603 abrogates the epirubicin-induced enrichment of TICs.In this study, researchers evaluated the small molecule Aurora kinase inhibitor AKI603 as a potential agent against TICs in breast cancer. AKI603 significantly inhibits Aurora-A (AurA) kinase and induced cell-cycle arrest. The activity of AurA may be a potential anti-TIC target for overcoming chemoresistance remains unclear.
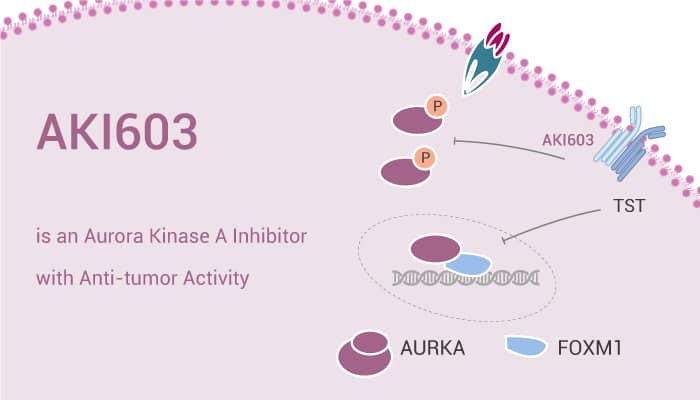
AKI603 inhibits AurA kinase and xenograft tumor growth. Moreover, AKI603 inhibits AurA activity, induces cell-cycle arrest, and suppresses proliferation in breast cancer cells. AKI603 inhibits AurA kinase activity with the IC50 of 12.3 nM. Treatment with 0.6 μM or higher concentrations of AKI603 for 48 hours significantly inhibits Thr288 phosphorylation. The total AurA protein levels are marginally reduced or not changed. Moreover, AKI603 also inhibits AurB kinase activity. The inhibitory activity of AKI603 toward AurB kinase is lower than that toward AurA kinase. Inhibition of AurA by AKI603 suppresses stem cell properties in breast cancer cells.
AKI603 (50 mg/kg, every day, by intragastric administration for 14 days) attenuates xenograft tumor growth in nude mice bearing MCF-7-Epi xenograft tumors. In addition, AKI603 shows low toxicity. The mice in the AKI603-treated group show a slight decrease in body weight during the experimental period.
In summary, inhibition of AurA kinase by AKI603 overcame chemoresistance through abolishing Tumor-initiating cells (TIC) in breast cancer, suggesting a novel strategy in cancer treatment.