Hu antigen R (HuR) is an RNA binding protein. Specifically, Its overexpression in human cancer is associated with aggressive disease, drug resistance, and poor prognosis. HuR is highly abundant in many types of cancer and promotes tumorigenesis through cancer-related mRNA interactions. Besides, HuR has related to the regulation of a variety of RNA properties, including stability, localization, and translation, as well as tumorigenesis. Drugs that disrupt the stabilizing effect of HuR on mRNA targets may have a huge impact on the growth and persistence of cancer inhibition.
HuR binds two RNA recognition motifs (RRM) RRM1 and RRM2 to its target. Moreover, HuR can bind to adenine and uridine rich elements (ARE) in the 3-untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNA to regulate its stability and translation. Furthermore, Drugs that disrupt the stabilizing effect of HuR on mRNA targets have a huge impact on the growth and persistence of cancer inhibition. Today, we will introduce a HuR-ARE interaction inhibitor, CMLD-2.
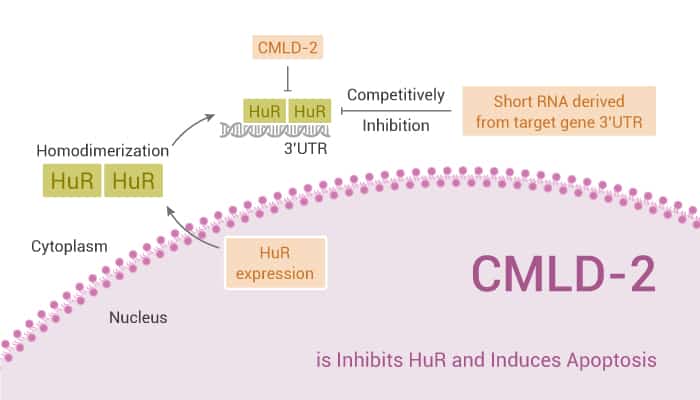
CMLD-2 is a HuR-ARE interaction inhibitor and induces apoptosis.
In the beginning, CMLD-2 competitively binds HuR protein disrupting its interaction with ARE-containing mRNAs (Ki=350 nM). Meanwhile, CMLD-2 exhibits antitumor activity in different cancer cells as colon, pancreatic, thyroid, and lung cancer cell lines.
Next, CMLD-2 (1-75 μM; 24-72 h) inhibits thyroid cancer cell, SW1736, 8505C, BCPAP, and K1 cells, viability. Nonetheless, CMLD-2 decreases directional migration capability and induces a strong decrease of MAD2 mRNA levels in these cells. Interestingly, CMLD-2 with 20-30 μM for 24-48 h activates caspases and induces apoptotic cell death in H1299 and A549 cells. Particularly, CMLD-2 induces G1 cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial perturbation in H1299 and A549 cells.
All in all, CMLD-2 is a HuR-ARE interaction inhibitor and induces apoptosis.
References:
Allegri , et, al. Sci Rep. 2019 May 14;9(1):7374.