MCTs (Monocarboxylate Transporters) are proton coupled monocarboxylate transporter. They can carry lactate and pyruvate across biological membranes. MCT1, also called SLC16A1, has a vital role in tumor cell energy homeostasis. Inhibition of lactate transport has effects on tumor growth. Cancer cells accumulate intracellular lactate if the lactate transport is inhibited. In turn, this decreases intracellular pH, and suppresses glycolysis. Therefore, to find out a potent MCT1 inhibitor is a need against cancer. BAY-8002 is a potent and selective monocarboxylate transporter 1 inhibitor. It blocks cellular lactate uptake and efflux in a MCT1 dependent manner.
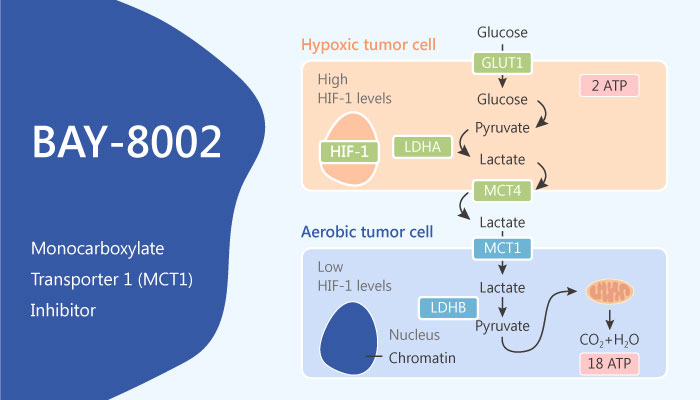
In order to find out the potential of the compound, researchers carried out a series of experiments to measure the bioactivity of BAY-8002.
Firstly, in cellular assays, BAY-8002 exhibits great potency. It has high protein binding activity. In cells, the compound has an IC50 of 85 nM. Besides, BAY-8002 effectively inhibits export of lactate in different cell lines. This causes growth inhibition of MCT-1 expressing lymphoma cells.
Secondly, in animal assay, researchers investigate the anti-tumor activity of BAY-8002. They choose Raji tumor-bearing mice as subjects of the study. The dose is 80 and 160 mg/kg, the route of administration is orally twice daily. As a result, BAY-8002 significantly prevents tumor growth. However, it shows no effect on tumor regression. Furthermore, the inhibitor increases intratumor lactate levels.
In a word, BAY-8002 is a potent, selective and orally active MCT1 inhibitor. It affects tumor growth via MCT1 inhibition. The latter blocks lactate transport. Scientists need more studies to discover the potential of BAY-8002 in cancer research.
References:
Quanz M, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Nov;17(11):2285-2296.