The stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is an innate pattern recognition receptor natively exists in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). STING has a great effect on host defense through supervising pathogenic or damage-associated nucleic acids.
Since the generation of optimal adaptive anti-tumor immune responses requires the STING signal, activation of the STING pathway is a promising approach to boost anti-cancer immunity.
Cyclic dinucleotides (CDNS) are second messenger molecules which are the exogenous bacterial origin.
CDNS ligands (2′,3′-cGAMP, et al) can directly bind to STING. Then, this process is able to activate and initiate a STING signaling cascade. As a result, it leads to the robust engagement of the interferon regulatory factor 3 (IFR3) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB) pathways. Furthermore, it ultimately stimulates the production of interferon-beta (IFN-β) and other pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Activation of the STING pathway and production of IFN-β are the critical components of the innate immune sensing of tumors. That is, it an important upstream event for optimal cytotoxic T-cell priming against tumor antigens.
It has been demonstrated that synthetic CDN agonists can achieve robust tumor regression.
Today, we will introduce another STING agonist, IACS-8803, a highly potent 2′,3′- thiophosphate CDN analog.
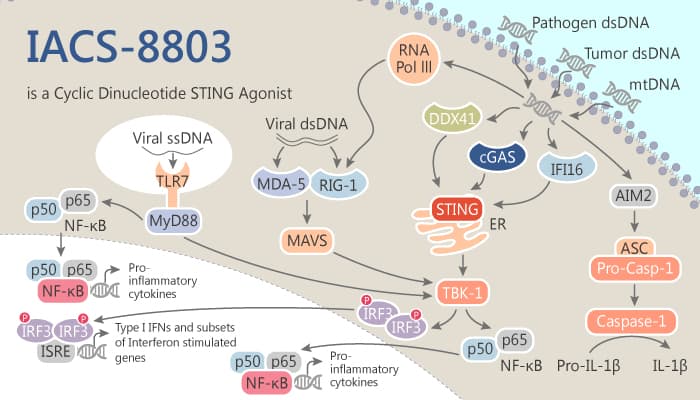
By comparing with the canonical 3′,3′-form, the 2′,3′-phosphodiester linkage offers improved affinity for STING.
The introduction of sulfur atoms within the two thiophophodiester bonds confers improves resistance to phophodiesterase-mediated degradation. Therefore, it results in enhanced activation of the STING pathway in vitro and significantly more robust antitumor responses in vivo.
IACS-8803 is a high-potency CDN STING agonist via a focused set of rationally selected modifications. As a CDN analog, it can exhibit robust activation of the STING pathway.
In the B16 murine model, comparing to the clinical benchmark ADU-S100, IACS-8803 (three intra-tumoral injections;10 μg, day 6, 9, 12 post-implantation) achieves superior regression on the untreated tumor in the contralateral flank, suggesting a more significant systemic immune response compared to the benchmark analog.
IACS-8779 treatment results in a higher number of mice cured of tumors compared to benchmarks.
In summary, targeting nucleobase and ribose modifications based on CDN analog has the potential to improve its antitumor efficacy and overall profile. And, IACS-8803, a highly potent cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist, has robust systemic antitumor efficacy.
reference:
Ager CR, et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Oct 15;29(20):126640.