The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK (MAPK) signal transduction pathway has attracted significant interest as a therapeutic target for cancer. ERK1/2 phosphorylates more than 50 downstream substrates responsible for cell growth, proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, and differentiation. Small molecule inhibitors of BRAF and MEK have shown promising activities in a variety of solid tumors clinically. The approved inhibitors including vemurafenib and cobimetinib as treatments for BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma validate the approach of targeting the MAPK pathway as an effective way of treating cancer. However, these drugs show limitations in the duration of efficacy for some patients with mutations.
ERK1 and ERK2 represent an essential node within the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling cascade. They are commonly activated by oncogenic mutations in BRAF or RAS or by upstream oncogenic signaling, such as receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activation. While targeting upstream nodes with RAF and MEK inhibitors has proven effective clinically, resistance frequently develops through reactivation of the pathway. Simultaneous targeting of multiple nodes in the pathway, such as MEK and ERK, offers the prospect of enhanced efficacy as well as reduced potential for acquired resistance. Scientists discovered and identified an orally bioavailable ERK kinase inhibitor Ravoxertinib (GDC-0994).
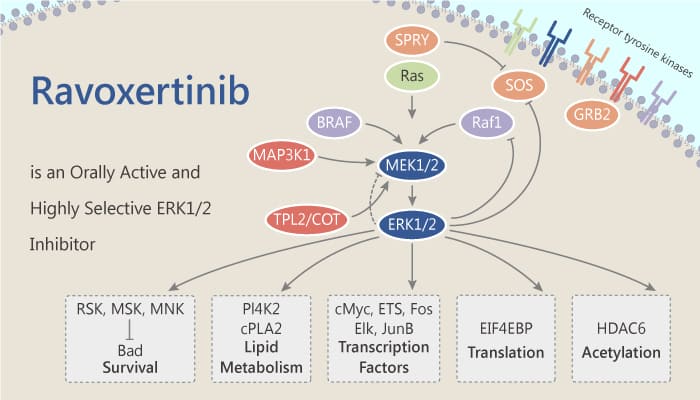
In vitro, Ravoxertinib (GDC-0994) also inhibits p90RSK with an IC50 of 12 nM. Besides, Ravoxertinib (GDC-0994) is highly selective for ERK1 and ERK2, with biochemical potency of 1.1 nM and 0.3 nM, respectively.
In vivo, in CD-1 mice, a 10 mg/kg oral dose of Ravoxertinib (GDC-0994) is sufficient to achieve the desired target coverage for at least 8 h. Oral dosing of Ravoxertinibdaily results in significant single-agent activity in multiple in vivo cancer models, including KRAS-mutant and BRAF-mutant human xenograft tumors in mice.
Ravoxertinib (GDC-0994) is currently in Phase I of clinical development.
Reference: