The paralogous chromatin regulators CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300 are factors critical for establishing and activating enhancer-mediated transcription.
The CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300 are important factors for activating enhancer-mediated transcription. These proteins consist of at least 10 distinct functional domains. Most of them interact with over 400 other proteins, including DNA-binding transcription factors, other chromatin regulators.
In addition to mediating protein-protein interactions on chromatin. p300/CBP also can exert enzymatic activity through a lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain.
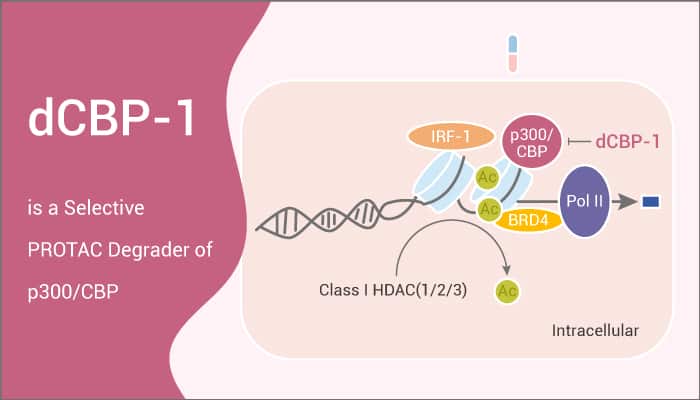
dCBP-1 is a potent and selective heterobifunctional degrader of p300/CBP based on PROTAC.
dCBP-1 induces degradation of large proteins, including BCR-ABL and SMARCA2/4. This demonstrates that chemical-induced proximity and ternary complex formation is readily achievable across a wide size range of proteins. However, when dCBP-1 is used for the first-order effects of p300/CBP loss. Besides, it should be restricted to short drug exposure times. prolonged treatment with dCBP-1 decreases IKZF1 and IKZF3 levels by direct degradation or transcription effects
dCBP-1 treatment shows near-complete degradation of p300/CBP in MM1S cells. However, dCBP-1 is also able to induce near-complete p300/CBP degradation across other multiple myeloma cell lines. Theos cell lines including MM1R, KMS-12-BM, and KMS34 cells. This compound is exceptionally potent at killing multiple myeloma cells and ablates oncogenic enhancer activity driving MYC expression.
Treatment of the human haploid cell line HAP1 with dCBP-1 reveals almost complete loss of both CBP and p300 between 10 and 1000 nM doses. A time-course analysis with 250 nM dCBP-1 revealed almost complete degradation of p300/CBP within an hour of treatment.
dCBP-1 is a useful tool for dissecting the acute effects of p300/CBP loss on enhancer structures. It also can detect transcription factor interactions, nucleosome remodeling, enhancer-promoter communication, and enhancer coordination of transcription activation.
In conclusion, dCBP-1 is a high-quality selective chemical inhibitor of p300/CBP function. It has the potential for cancer therapeutics research.
Reference:
Raghu Vannam, et al. Cell Chem Biol. 2020 Dec 31;S2451-9456(20)30513-4.