A study from Victoria K Woodcock suggested that AZD0424 is an inhibitor of the proto-oncogenic non-receptor tyrosine kinases Src and ABL1. The kinase plays an indefensible role in cancer. Src expresses lowly in the majority of cell types and participates in regulating bone metabolism, proliferation, and angiogenesis. Src also plays a role in the regulation of cell invasion and metastasis in cancer, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colon cancer. In addition, Src expression relates to advanced malignancy and poor prognosis in a variety of cancers including colorectal carcinoma and osteosarcoma. Moreover, the upregulation of Src expression and/or signaling is associated with resistance to many classes of anti-cancer drugs including those targeted against HER-2 and EGFR. While ABL1 kinase also represents a potential target with relevance in solid tumors.
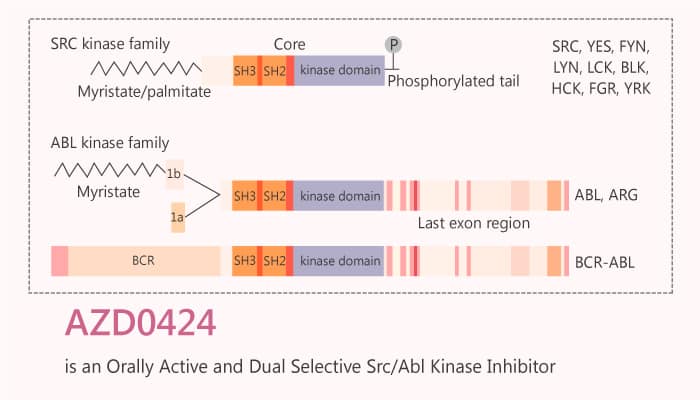
In general, AZD0424 is an orally active and dual selective Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Moreover, AZD0424 induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in lymphoma cells.
In vitro, AZD0424 (1-5 μM; 24-48 hours) is emerged to be the more effective of the three tested inhibitors (AZM559756, AZD0530, and AZD0424), inducing the highest levels of apoptosis with the lowest concentrations in lymphoma cells.
Additionally, AZD0424 (5 μM; 48 hours) leads to increased G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in DOHH-2 and WSU-NHL cells. While the cell cycle progression of the nonsensitive cell lines Raji and Jurkat remain unaffected.
In vivo, No significant post-administration changes in CTX or NTX level happened in the single patient who received AZD0424 with a dose of 5 mg. Greater percentage reductions in CTX and NTX levels happened at doses of more than 10 mg per day of AZD0424 than that achieved with 50 mg per day of saracatinib and for NTX, similar to that achieved with 125 or 175 mg per day of saracatinib.