B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is a transcriptional repressor that interacts with its corepressors BcoR and SMRT. Since this protein-protein interaction (PPI) induces activation and differentiation of B lymphocytes, BCL6 is an attractive drug target for potential autoimmune disease treatments. In addition, BCL6 acts as a master regulator of germinal center B cell differentiation that leads to the production of autoantibodies. Besides, BCL6 dimerizes and exposes a surface groove at the interface of two helix chains. Moreover, BCL6 dimerizes and exposes a surface groove at the interface of two helix chains. This role suggests that BCL6 inhibitors would be good drug candidates for treating autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, The BCL6 binding of rifamycin SV was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy. F1324 is a potent and high-affinity peptidic inhibitor of BCL6 with anti-cancer activity.
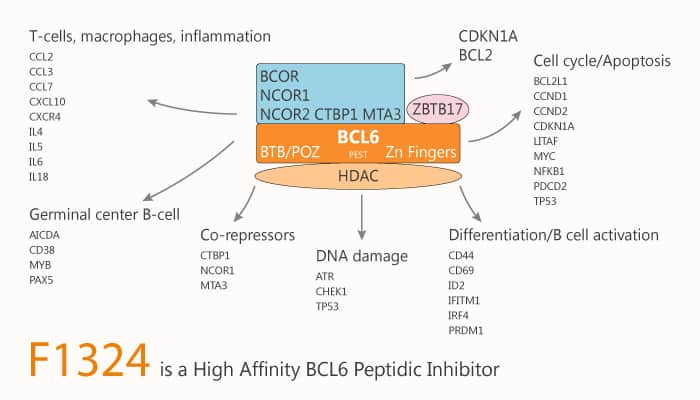
F1324 is a potent, high-affinity peptidic inhibitor of B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) with an IC50 of 1 nM. Specifically, F1324 (Ac-LWYTDIRMSWRVP-OH) exhibits a binding t1/2 value of 441 s and has strong inhibition activity against BCL6 PPI. Meanwhile, the high affinity of F1324 was caused by the effective interaction of its side chains while its main chain structure was similar to that of BcoR (Arg498-514Pro). Nonetheless, F1324 is the strongest inhibitor with the highest affinity against BCL6 in a cell-free assay. Finally, F1324 is a potent peptidic inhibitor, with nanomolar inhibitory activity. To our knowledge, F1324 is the strongest BCL6-binding peptide yet reported. All in all, F1324 is a potent and high-affinity peptidic inhibitor of BCL6 with anti-cancer activity.
References:
Sakamoto K, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Jan 8;482(2):310-316.