Apoptosis is a distinctive form of cell death exhibiting specific morphological and biochemical characteristics, including cell membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, genomic DNA fragmentation, and exposure of specific phagocytosis signaling molecules on the cell surface. Cells undergoing apoptosis differ from those dying through necrosis. Necrotic cells are usually recognized by the immune system as a danger signal and, thus, resulting in inflammation. In contrast, apoptotic death is quiet and orderly.
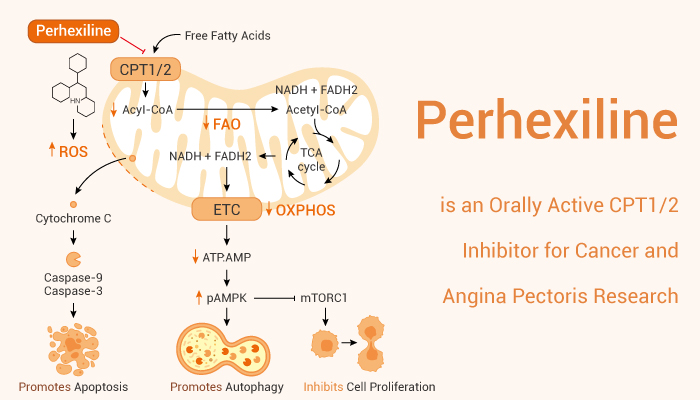
Perhexiline is a CPT1/2 inhibitor and Induces Apoptosis for Cancer and Angina Pectoris Research
Perhexiline is an orally active CPT1 and CPT2 inhibitor that reduces fatty acid metabolism. And Perhexiline induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in hepatic cells. And it can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) and shows anti-tumor activity. Perhexiline can be used in the research of cancers, and cardiovascular disease like angina.
In Vitro, Perhexiline (5-25 μM, 2-6 h) reduces cell viability in HepG2 cells. Morever, it (5-25 μM, 2-6 h) reduces cellular ATP content and Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in HepG2 cells. In addition, Perhexiline (20 μM, 2 h) activates caspase 3/7 in HepG2 cells. Perhexiline (5-25 μM, 4 h) causes mitochondrial dysfunction in HepG2 cells. What’s more, Perhexiline (5 μM, 48 h) selectively induces massive apoptosis in CLL cells (high expression of CPT). In Vivo, Perhexiline (200 mg/kg, p.o., daily for 8 weeks) reduces peripheral neural function in female DA rats. Perhexiline (80 mg/kg, oral gavage, for 3 days) demonstrates anti-tumor activity in glioblastoma mouse model.
In conclusion, Perhexiline is an orally active CPT1/2 inhibitor for cancer and angina pectoris research.
Reference:
[1]. Chronic Coronary Artery Disease, 2018, 412-431.
[2]. Toxicol In Vitro. 2020 Dec;69:104987.
[3]. Oncogene. 2016 Oct 27;35(43):5663-5673.