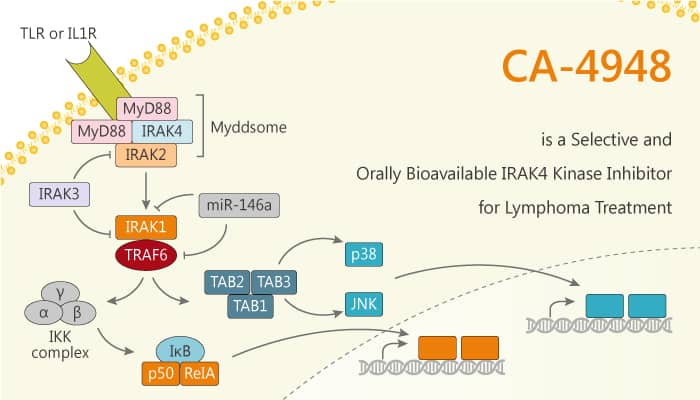
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is the most upstream kinase in Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) signaling. Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling in a variety of myeloid and lymphoid cell types require IRAK4 kinase activity. The MYD88 adaptor protein facilitates the recruitment of IRAK4 to these receptors and its subsequent activation. In Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cases, the MYD88 adaptor protein mutation is in ~22% of DLBCL cases. Moreover, the MYD88 L265P activating mutation is in ~30% of the activated B-cell (ABC) and ~6% of germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtypes of DLBCL. Moreover, it leads to the constitutive activation of NF-κB signaling. Thus, the development of small-molecule inhibitors targeting IRAK4 is an attractive anticancer strategy for MYD88 mutation-containing cancers. CA-4948 is a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable IRAK4 kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of <50 nM.
CA-4948 is a selective and potent IRAK4 kinase inhibitor with in vivo activity in a TLR4-induced cytokine release model. It exhibits favorable drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics (DMPK) properties, oral bioavailability, and is well tolerated in mice. Meanwhile, CA-4948 exhibits dose-dependent efficacy in activated B-cell (ABC)-DLBCL MYD88-L265P xenograft tumor models using cell lines OCI-LY3 and OCI-LY10. CA-4948 exhibits the greatest efficacy in four of the five ABC-DLBCL PDX models tested as compared to GBC-DLBCL and ABC/GCB DLBCL patient-derived DLBCL tumor xenograft (PDX) models. Furthermore, CA-4948 is efficacious in ABC-DLBCL PDX tumors, and it contains activating mutations in both TLR/IL-1R and BCR signaling pathways (MYD88 and CD79B double mutants).
All in all, CA-4948 has the therapeutic potential of IRAK4 kinase inhibition. As a single-agent or in combination with BCR inhibitors, CA-4948 is for the treatment of DLBCL.
Reference:
Robert N. Booher, et al. AACR Annual Meeting 2017; April 1-5, 2017.