Mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) is a very aggressive blood cancer that predominantly occurs in pediatric patients. Especially, MLL is acute leukemia with poor prognosis. Spontaneous translocations at the MLL1 gene cause MLL. MLL fusions bind with a high affinity to the nuclear protein Menin. Menin-MLL interaction enables leukemic transformation by driving a specific transcription program. SNDX-5613 is a potent, orally active inhibitor of the high-affinity interaction site on menin with the protein MLL1.
Mixed-lineage acute leukemias represent a heterogeneous category of rare, poorly differentiated acute leukemias that possess characteristics of both lymphoid and myeloid precursor cells. The menin-MLL complex plays a key role in the survival, growth, transformation, and proliferation of certain kinds of leukemia cells. Moreover, Menin-MLL interaction inhibitors show robust treatment benefits in multiple preclinical models of NPM1 mutant AML.
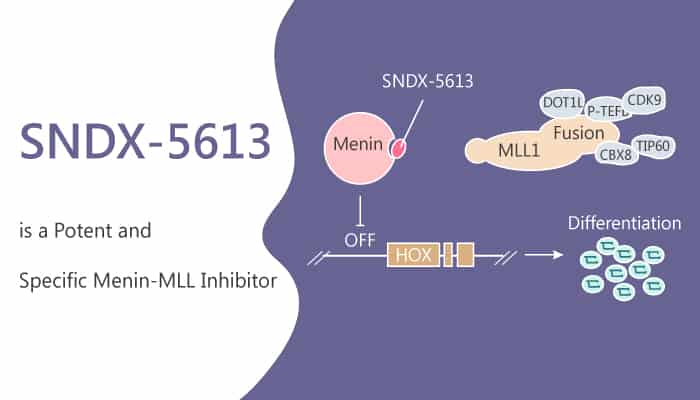
SNDX-5613 is a small molecule inhibitor that blocks MLL1 and Menin in certain cells. SNDX-5613 is an orally bioavailable protein-protein interaction (PPI) inhibitor of the MLL proteins, with potential antineoplastic activity. In particular, SNDX-5613 can induce a response in patients with genetically-defined acute leukemias. Upon oral administration, SNDX-5613 targets and binds to the nuclear protein menin, thereby preventing the interaction between the two proteins menin and MLL and the formation of the menin-MLL complex. This reduces the expression of downstream target genes and results in an inhibition of the proliferation of MLL-rearranged leukemic cells. In preclinical models of MLL acute leukemias, SNDX-5613 demonstrates robust, dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth, resulting in a marked survival benefit.
All in all, SNDX-5613 is a potent, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of the Menin-MLL binding interaction for the research of MLL-rearranged (MLL-r) acute leukemias, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).