The importance of angiogenesis in solid tumor growth is well established. Inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor (VEGFR) pathway is now an approved and generally accepted treatment of lung cancer.
Interestingly, bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody against VEGF-A, is predominantly administered in combination with chemotherapy, whereas the small-molecule inhibitors of the VEGFRs, sunitinib and sorafenib, are used as single agent. Therefore, we main introduce the character of telatinib in cancer research, or in combination with other chemical agents.
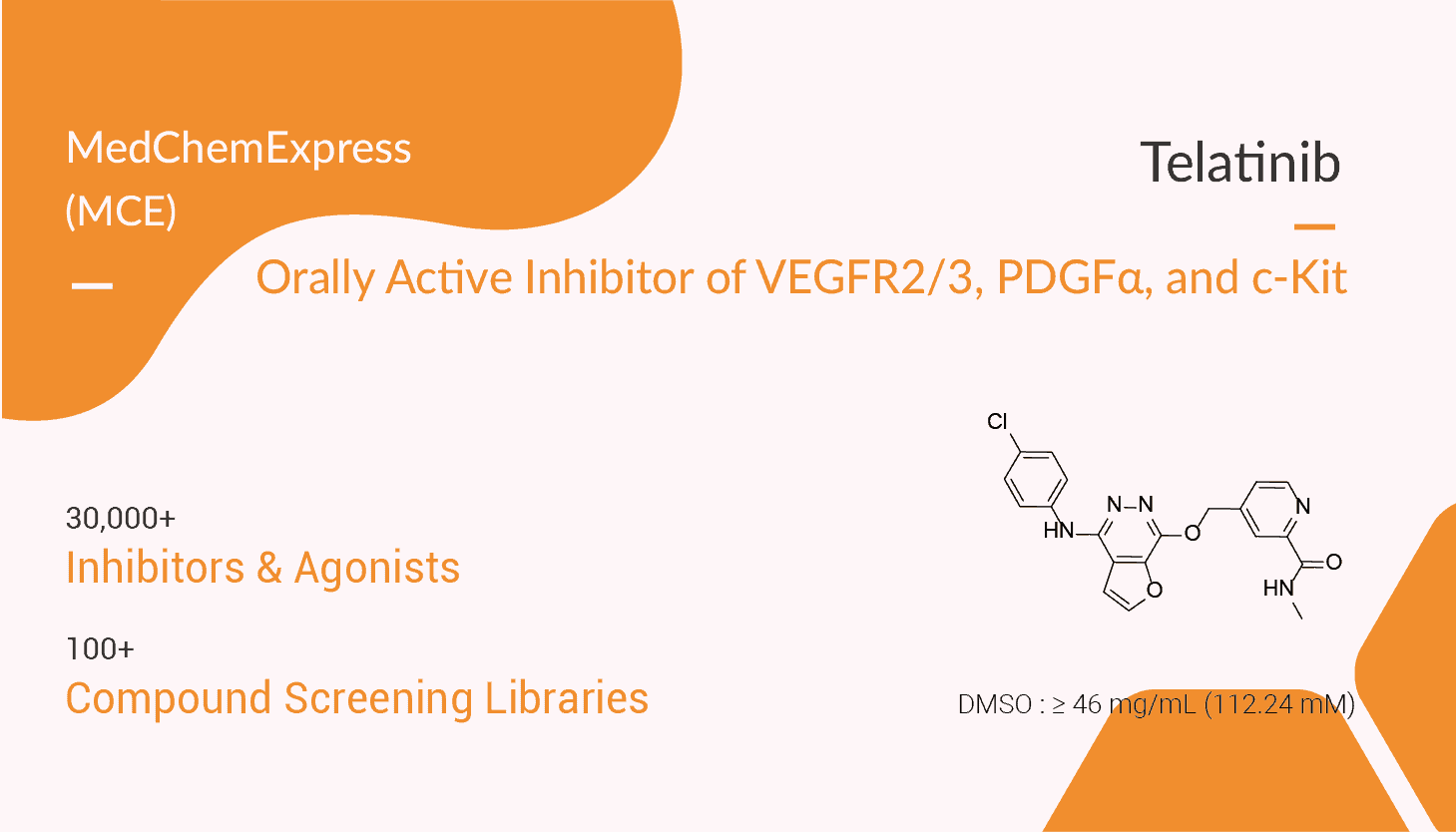
Telatinib is an orally active inhibitor of VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFα, and c-Kit with IC50s of 6, 4, 15 and 1 nM, respectively.
Telatinib has low affinity for the Raf kinase pathway, EGFR family, the FGFR family, or the Tie-2 receptor. It is metabolized by various cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms including CYP3A4/3A5, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 as well as by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A4 (UGT1A4), with the formation of the N-glucuronides of telatinib as the major biotransformation pathway. In addition, in vitro studies show telatinib to be a weak substrate of the adenosine triphosphate binding cassette (ABC) B1 (ABCB1) transporter. Telatinib at 1 μM significantly enhances the intracellular accumulation of [3H]-mitoxantrone (MX) in ABCG2-overexpressing cell lines.
Telatinib causes a significant decrease in endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasodilation. VEGF inhibition by itself decreases NO synthesis, which promotes vasoconstriction, increases peripheral resistance, and therefore can induce an increase in blood pressure. Telatinib (15 mg/kg) with doxorubicin (1.8 mg/kg) significantly decreases the growth rate and tumor size of ABCG2 overexpressing tumors in a xenograft nude mouse model.
In conclusion, Telatinib has the potential for the research of cancer disease or in combination with other agents. This still needs further research.
Reference: