Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as SLC2A1), is a member of membrane transport proteins. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose across the plasma membranes of mammalian cells. Low glucose levels can promote GLUT1 expression in cell membranes. GLUT1 is also a major receptor for the uptake of Vitamin C as well as glucose, especially in non-vitamin C-producing mammals as part of an adaptation to compensate by participating in a Vitamin C recycling process. It can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II in the cell membrane and on the cell surface.
The classical effects of GLUT1 deficiency include infantile drug-resistant seizures, mild to severe developmental delay, and microcephaly. The diagnosis is suggested by hypoglycorrhachia (a cerebrospinal fluid glucose value of <2.2 mmol/L with a cerebrospinal fluid-plasma glucose ratio of generally <0.4). The ketogenic diet is effective for this disease because ketone bodies easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier and serve as an alternative fuel for the brain.
STF-31 is a potent and selective inhibitor of GLUT1.
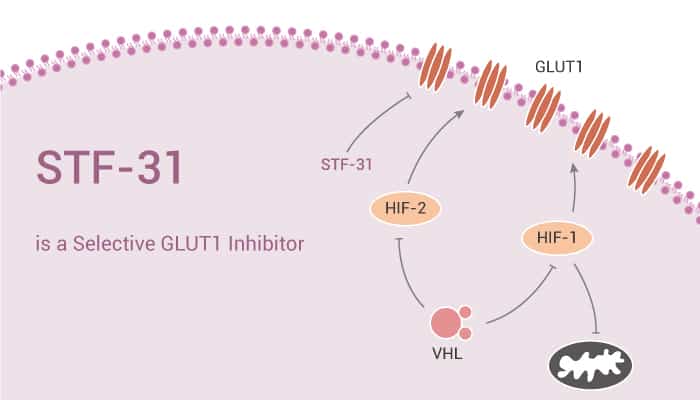
STF-31 can inhibit glucose uptake in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) 4 cells. Besides, STF-31 causes necrotic cell death in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)-deficient RCC cells. It decreases oxidative phosphorylation of aerobic glycolysis and leads to necrosis. Meanwhile, STF-31 does not induce autophagy, apoptosis, or DNA damage. STF-31 is also a NAMPT inhibitor. It does not bind to other glucose transporters and does not inhibit a broad range of 50 tested. In vivo, STF-31 reduces light-induced CX3CR1gfp+/+ mice microglial activation and retinal degeneration. What’s more, STF-31 does not affect normal mice’s body weight, behavior, and ERG responses.
All in all, STF-31 is a potent and selective inhibitor of GLUT1 that inhibits glucose uptake in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) 4 cells.
References:
[1] Morioka S, et, al. Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7733):714-718.
[2] Cao S, et, al. Future Med Chem. 2021 Jul;13(14):1227-1243.