IL-15 is an inflammatory cytokine, as well as an activator of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. It binds to and signals in a complex consisting of the IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain (γ, CD132). The IL-15 receptor (IL15Rβγ) is constitutively expressed on NK cells and is a central cytokine for enhanced function. When IL15Rβγ recognizes IL-15 presented by helper cells, it stimulates and strengthens NK cell ADCC. This signal also amplifies ADCC directed by anti-CD20 mAb. IL-15 signaling also increases co-stimulation of NK cell-derived cytokines (eg, IFNγ), increases expression of cytotoxic effector molecules, enhances proliferation and survival, and increases motility. Activation of IL-15 is effective against B-cell lymphoma innate immune responses. Here, we will introduce a potent IL15 superagonist, Inbakicept (ALT-803). It can effectively present IL-15 without helper cells and suppresses lymphoma.
Inbakicept is an IL-15 superagonist complex, involved in cancer research.
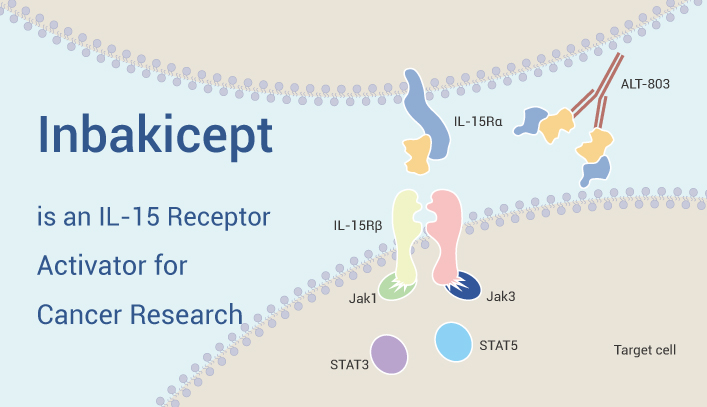
Inbakicept is an IL-15 superagonist complex consisting of an IL-15 mutein bound to the sushi domain of IL-15Rα. IL-15Rα, on the other hand, fuses with the Fc region of IgG1. Specifically, Inbakicept (0.01-1 nM; 20 h) enhances the cytotoxicity of human NK cells and kills K562 target cells. Inbakicept (0.01-1 nM; 24 h) also dose-dependently enhances the expression of cytotoxic effector molecules. Including perforin (Prf1) and granzyme B (GzmB) protein or cell surface CD69 expression in CD56dimCD16+ NK cells. Inbakicept also dose-dependent augments IFNγ production and degranulation (CD107a surface expression) in rituximab-coated Raji cells.
In vivo studies, Inbakicept can promote NK cell proliferation in mice. It (0.2 mg/kg; iv; twice weekly for 2 weeks) also enhances the protection of the anti-CD20 mAb, Rituximab, against lethal Daudi’s lymphoma in a mouse model. Its anti-lymphoma effect in vivo is closely related to the activation of NK cells.
In summary, Inbakicept is an IL15 superagonist, enhancing the immune anti-tumor effect of anti-CD20 mAb. By promoting NK cell proliferation and activation, promoting degranulation,
and IFNγ production, it kills lymphoma cells in mouse models.
Reference:
[1] Rosario M, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 1;22(3):596-608.