Tumor-induced angiogenesis, or the formation of new capillary networks between neoplastic cells and endothelial cells of the host, is required for solid tumor growth and metastases. In addition, the Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) is an important receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) in the induction of angiogenesis. As a key stimulator of tumor angiogenesis, VEGF promotes endothelial cell proliferation, survival, migration, invasion, and differentiation. However, abnormal activation of VEGFR leads to several disorders including cancer. Therefore, the VEGF signaling pathway has been the target of extensive drug discovery research. In addition, the 2-aminothiazole scaffold has emerged as a promising scaffold in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery research. Hence, we will introduce BMS-605541, a selective and orally active inhibitor of VEGFR-2 kinase.
BMS-605541 is a selective and orally active VEGFR-2 inhibitor, with an IC50 value of 23 nM and a Ki value of 49 nM, respectively.
BMS-605541 inhibits the growth of HUVECs through VEGF with an IC50 value of 25 nM, in vitro experiments. In addition, BMS-605541 inhibits the activity of Flk-1, VEGFR-1, and PDGFR-β with IC50 values of 40 nM, 400 nM, and 200 nM, respectively.
In vivo, BMS-605541 (12.5-180 mg/kg; p.o.; once a day or twice a day for 14 days) has anti-tumor activity, in thymic mice subcutaneously implanted with L2987 and HCT-116 xenografts. Moreover, BMS-605541 illustrates a favorable pharmacokinetic profile; a moderate steady-state volume of distribution, low systemic clearance, favorable half-life, and mean residence times. Also, BMS-605541 shows 100% and 52% oral bioavailabilities in mice and monkeys, respectively.
All in all, BMS-605541 is a promising VEGFR-2 inhibitor. BMS-605541 not only shows good kinase selectivity in vitro but also demonstra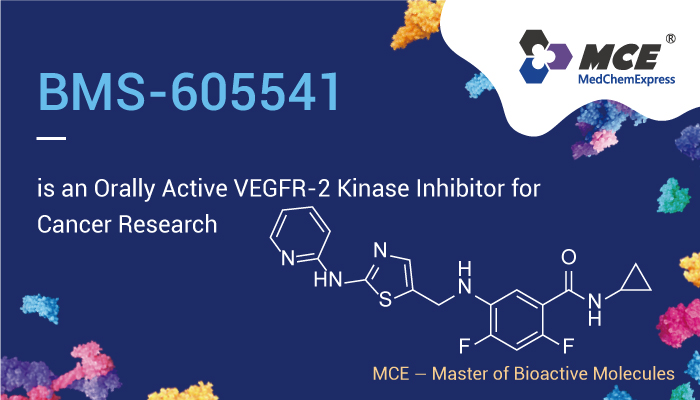 tes favorable pharmacokinetic properties in multiple species. Moreover, BMS-605541 also has robust in vivo efficacy in human lung and colon carcinoma xenograft models.
tes favorable pharmacokinetic properties in multiple species. Moreover, BMS-605541 also has robust in vivo efficacy in human lung and colon carcinoma xenograft models.
Reference:
- Borzilleri RM, et al. J Med Chem. 2006 Jun 29;49(13):3766-9.
- Alizadeh SR, et al. Med Chem Res. 2021;30(4):771-806.
- Xu D, et al. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011 Jan;11(1):18-31.