Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) metabolism pathway plays a critical role in supporting tumor cell proliferation. It can orchestrate the tumor microenvironment by providing bioenergy and directing macromolecular synthesis. In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. However, increasing evidence shows that certain cancer subtypes are metabolically dependent on OXPHOS for survival and growth but not glycolysis. The OXPHOS components consist of complexes I-V. Complexes I-IV, known as the electron transport chain (ETC), are responsible for transferring electrons from donors to oxygen and generating a proton gradient between the mitochondrial matrix and the intermembrane space. Among them complex I plays a central role in the entire process of OXPHOS.
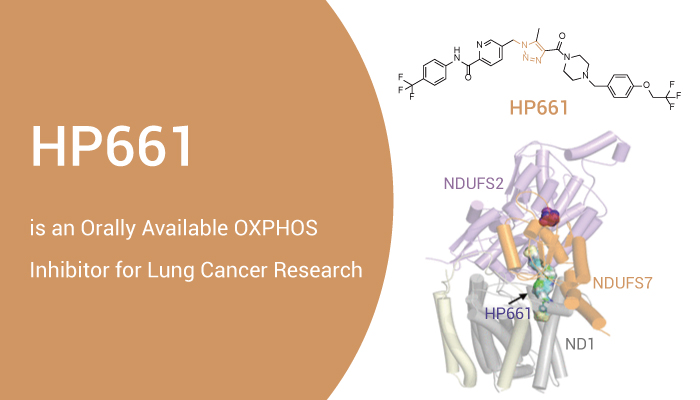
HP661 is a highly potent and orally active 1H-1,2,3-triazole oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibitor.
In addition, HP661 selectively blocks the activity of mitochondrial complex I and reduces the production of the ROS. Moreover, HP661 specifically compromised the mitochondrial oxygen consumption of high-OXPHOS lung cancer cells. Meanwhile, it does not affect mitochondrial oxygen consumption in low-OXPHOS lung cancer cells or normal cells. Besides, HP661 selectively inhibits the proliferation of high-OXPHOS lung cancer cells in the submicromolar range. HP661 selectively inhibits the OXPHOS function of lung cancer cells but has little impact on glycolysis in the low nanomolar range. Furthermore, HP661 exhibits weak inhibition activity on CYP2C9, whereas it has no apparent effects on other main CYP enzymes, including CYP1A, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4-M.
Importantly, in a mouse model of high-OXPHOS lung cancer, HP661 significantly suppresses tumor growth by oral dosing. When noted, HP661 exhibits favorable tolerance in vivo. Thus, HP661 abrogates the growth of high OXPHOS-dependent tumors, conquers high OXPHOS-mediated drug resistance, and induces cell apoptosis.
To sum up, HP661 is a potent and orally active OXPHOS inhibitor with anticancer effects.
References:
[1] Peng He, et al. J Med Chem. 2023 May 11;66(9):6047-6069.