Pancreatic cancer accounts for the second highest number of cancer deaths. The 5-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer is very low. Approximately 85% of pancreatic cancers are pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC).
Many genes is implicated with PDAC. Two of the most familiar mutated genes are the KRAS oncogene and TP53 tumor suppressor gene. KRAS encodes an oncoprotein in PDAC cells and the TP53 encodes a tumor suppressor oncoprotein in the cells. The TP53 tumor suppressor is mutated in ~75% of pancreatic cancers. The mutant TP53 protein in PDAC promotes tumor growth and metastasis.
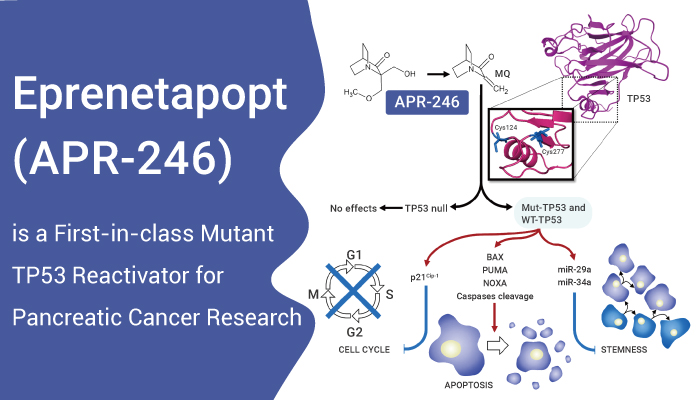
APR-246 is a mutant TP53 reactivator. It can restore some of the properties of wild-type (WT) TP53.
Eprenetapopt (APR-246) is a first-in-class mutant TP53 reactivator for pancreatic cancer research
Eprenetapopt (APR-246) is a first-in-class, small molecule that restores wild-type p53 functions in TP53-mutant cells. Cellular TrxR1 activity is inhibited by Eprenetapopt irrespective of p53 status. Eprenetapopt can directly affect cellular redox status via targeting of the selenoprotein TrxR1. Second, Eprenetapopt promote correct folding of mutant p53.
Eprenetapopt can reactivate mutant forms of the p63 and p73 proteins that share high structural homology with p53. Third, Eprenetapopt is a powerful apoptosis-inducing agent. Eprenetapopt can enhance apoptosis in mutant p53 carrying cells, and inhibit tumor growth in mice.
However, Eprenetapopt can also act independently of the p53 status of the cell. It radiosensitize prostate carcinoma cell lines with mutant or wild type p53 and p53-/- cells as well. Introduction of mutant p53 into p53-/- hepatocarcinoma cells increases sensitivity to Eprenetapopt without the induction of p53 target genes. Eprenetapopt regularly induces apoptosis in mutant p53 expressing cells.
Reference:
[1] Abrams SL, et al. Cells. 2022 Feb 24;11(5):794.
[2] Peng X, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 24;4(10):e881.