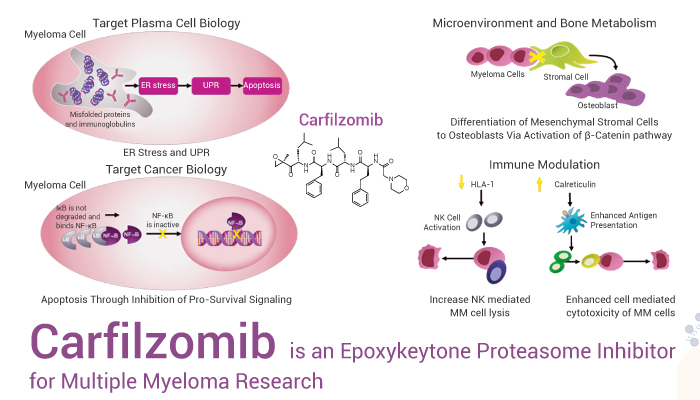
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is characterized by the production of monoclonal immunoglobulin (Ig), which may be detected in serum or urine, and tumor cell tropism for the bone marrow (BM). Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor (PI) that irreversibly binds the proteasome. NF-κB induce immunogenic myeloma cell death through enhanced antigen presentation and increased natural kill cell-mediated MM-cell lysis. Carfilzomib has synergistic activity with proteasome inhibitors (PIs) by enhanced proteasome targeting, caspase activation, and NF-κB inhibitory activity. Hence, we introduce Carfilzomib, a sustained proteasome inhibitor and do not decrease the neurite length or inhibit nonproteasomal targets.
Carfilzomib has anti-MM activity in vitro and in vivo
In vitro, Carfilzomib (0-100 nM, 24 h) inhibited proteasome activity in RPMI-8226 cells. Carfilzomib decreased the viability of MM cell lines and MM patient-derived CD138+ cells when treated for 24 h. Besides, Carfilzomib accumulated polyubiquitinated proteins in MM cells.
In vivo, Carfilzomib (4 mg/kg, i.v., twice a week) inhibited tumor growth compared with control group in tumor BALB/c nude mice model. Also, Carfilzomib inhibited pathological bone destruction in patients with MM. When compared to the control treatment, carfilzomib and D395 both dramatically inhibited outward potassium currents in a dose-dependent manner.
In summary, Carfilzomib is a selective proteasome inhibitor that has remarkable anti-MM activity in vitro and in vivo.
Reference:
[1] Leukemia. 2019 Sep;33(9):2127-2143.
[2] Cell Death Dis. 2021 Apr 30;12(5):429.