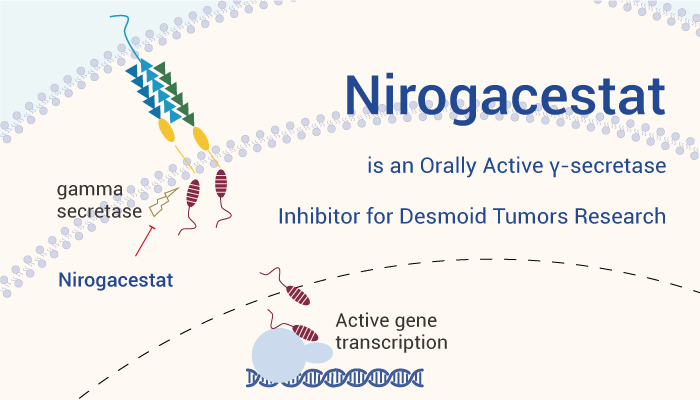
On November 27, 2023, the Food and Drug Administration approved Nirogacestat for adult patients with progressing desmoid tumors who require systemic treatment. Nirogacestat blocks the activity of an enzyme called gamma secretase. It is involved in driving desmoid tumor growth. This is the first approved treatment for desmoid tumors.
Nirogacestat (PF-3084014) is a reversible, orally bioavailable, noncompetitive, and selective γ-secretase inhibitor with an IC50 of 6.2 nM.
Nirogacestat (PF-03084014) has γ-secretase enzyme inhibition with an IC50 of 6.2 nM in cell-free assay for Aβ production. Second, the cell IC50 is 13.3 nM in cellular assays using HPB-ALL cells. In addition, Nirogacestat (7 day) causes a significant increase in caspase-3 activities in HPB-ALL and TALL-1 cells as well as an induction of cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3.
In vivo: First of all, Nirogacestat shows robust antitumor activity in model on 14-day twice daily dosing. Meanwhile, tumor growth inhibition is dose dependent, with maximal tumor growth inhibition of ~92% obtained at high dose levels (150 mg/kg). Finally, in tumor growth inhibition studies, Nirogacestat (< 100 mg/kg; twice daily dosing for more than a week) is well tolerated and no significant weight loss, morbidity, or mortality is observed. However, Nirogacestat (150 mg/kg; 10 days) causes mice have diarrhea and show weight loss (10-15%). And the toxicity of Nirogacestatis reversible.
In a word, Nirogacestat is an orally active γ-secretase inhibitor for desmoid tumors research.
Reference:
[1] Wei P, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Jun;9(6):1618-28.