Akt, also known as PKB, is a serine threonine protein kinase with three subtypes: Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3. Specifically, AKT belongs to the cAMP dependent, cGMP dependent, and protein kinase C (AGC) protein kinase subfamily. Besides, Akt kinase plays a core role in transmitting extracellular cues to various cellular compartments, thereby executing these biological processes. Moreover, AKT has a wide range of downstream effectors involved in cell survival and proliferation. AKT is activated through phosphorylation on Thr308 or Ser473. Furthermore, it phosphorylates various downstream protein substrates, including GSK3 β、 Bcl-2 related death promoter, forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma, and mouse dual minute 2 homolog. The PI3K-AKT pathway is one of the most common dysregulated pathways in all cancers. For example, it causes somatic mutations, copy number changes, abnormal epigenetic regulation, and increased expression in many cancers. The abnormal overexpression of p-AKT is a common feature of early and late stage cancers. Here, we will introduce an oral Akt inhibitor, Perifosine.
Perifosine is an Orally Active Akt Inhibitor for Kinds of Cancers Research.
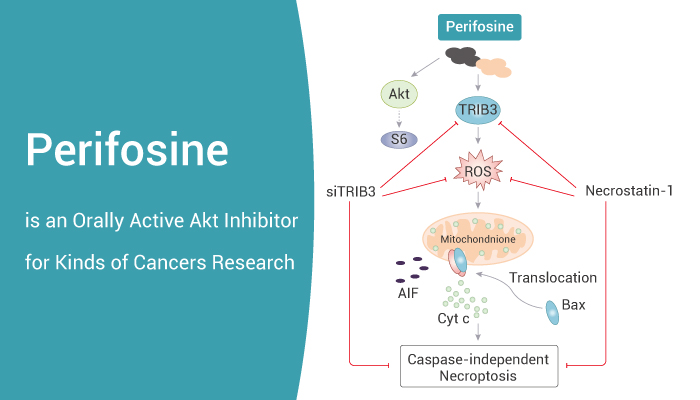
To begin with, Perifosine inhibits proliferation of different tumor cell lines with IC50s of 0.6-8.9 μM. Meanwhile, Perifosine blocks cell cycle progression of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells at G1-S and G2-M by inducing p21WAF1. Nonetheless, Perifosine induces both G1-S and G2-M cell cycle arrest, together with p21WAF1 expression in both p53 wild-type and p53-/- clones.
Secondly, Perifosine markedly decreases p-Akt from 10 min to 24 hours and subsequently, moderately decreased p-S6 from 1h to 24 h after injection in mice. Most importantly, the tumors treated with Temozolomide+Perifosine have the lowest Ki-67 staining index.
All in all, Perifosine is an orally active Akt inhibitor for kinds of cancers research.
References:
[1] Vyomesh Patel, et al. Cancer Res, 2002, 62(5), 14.
[2] Chen L, et al. Epilepsia. 2012 Nov;53(11):2026-33.