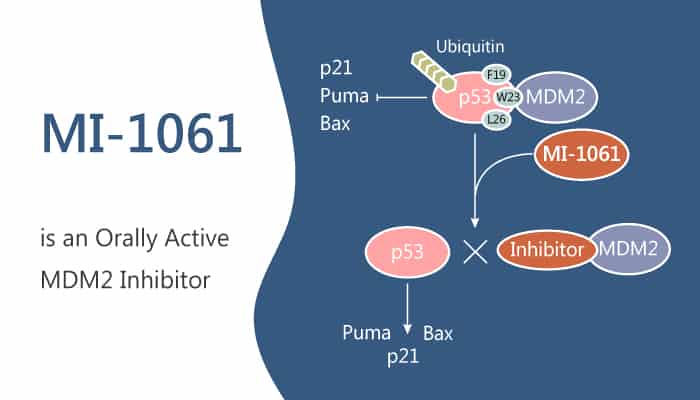
Inhibition of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction is being actively pursued as a new anticancer therapeutic strategy. Our previous blogs have introduced typical MDM2 or MDM2-p53 inhibitors, including MI-773, RG7112, and AMG 232. Today, I would like to mention another MDM2 inhibitor MI-1061 came from a study from Aguilar A.
MI-1061 is a chemically stable, potent, and efficacious MDM2 inhibitor. MI-1061 is a potent and orally bioavailable MDM2 (MDM2-p53 interaction) inhibitor (IC50=4.4 nM; Ki=0.16 nM). Furthermore, MI-1061 potently activates p53, induces apoptosis, and has anti-tumor activity.
In vitro, MI-1061 achieves IC50=100 and 250 nM in the SJSA-1 and HCT-116 p53+/+ cell lines, respectively, and has IC50>10000 nM in the p53 knockout cell line HCT-116 p53–/–cell line.
In vivo, the authors evaluated MI-1061 for its ability to activate p53 in a PD experiment in the SJSA-1 tumor tissue harvested from mice. The animals treated with a single, oral dose of each compound at 100 mg/kg as indicated. As a result, MI-1061 effectively activated p53, leading to the accumulation of p53, MDM2, and p21 proteins. MI-1061 effectively induced robust cleavage of PARP in the tumor, indicative of strong apoptosis induction. Besides, consistent with the strong p53 activation and apoptosis induction in the tumor tissue, MI-1061 demonstrated strong antitumor activity and achieved significant tumor regression when administered orally daily for 14 days at 100 mg/kg. of note, all the mice treated with MI-1061 suffered no weight loss and did not show any signs of toxicity during or after the treatment.