The fluoropyrimidine 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is an antimetabolite drug that is widely used for the treatment of cancer, particularly for colorectal cancer. Fluorouracil is part of a group of chemotherapy drugs known as anti-metabolites. Anti-metabolites are similar to normal body molecules but they have a slightly different structure. These differences mean that anti metabolites stop cancer cells working properly. They stop the cells making and repairing DNA. Additionally, 5-FU exerts its anticancer effects through inhibition of thymidylate synthase and incorporation of its metabolites into RNA and DNA.
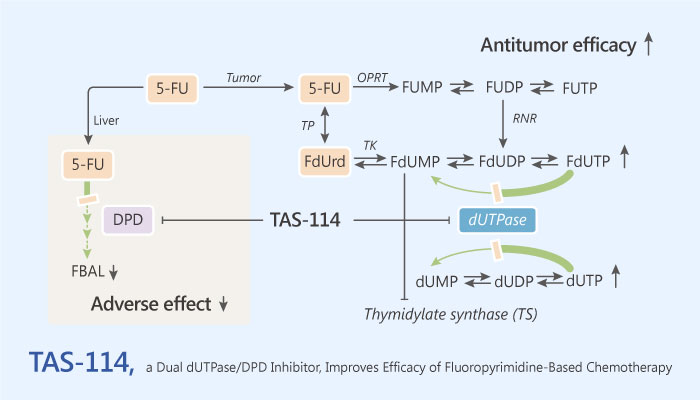
Yano et al has identified a dual dUTPase/DPD inhibitor TAS-114. It strongly and competitively inhibited dUTPase and enhanced the cytotoxicity of fluoropyrimidines in cancer cells. However, it had little intrinsic activity. TAS-114 also had moderate and reversible inhibitory activity on dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, a catabolizing enzyme of 5-FU. Thus, TAS-114 increased the bioavailability of 5-FU when coadministered with capecitabine in mice, and it significantly improved the therapeutic efficacy of capecitabine by reducing the required dose of the prodrug by dual enzyme inhibition. Enhancement of antitumor efficacy caused by the addition of TAS-114 was retained in the presence of a potent DPD inhibitor containing oral fluoropyrimidine (S-1), indicating that dUTPase inhibition plays a major role in enhancing the antitumor efficacy of fluoropyrimidine-based therapy.
In conclusion, TAS-114, a dual dUTPase/DPD inhibitor, demonstrated the potential to improve the therapeutic efficacy of fluoropyrimidine. Dual inhibition of dUTPase and DPD is a novel strategy for the advancement of oral fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for cancer treatment.