FGFR (Fibroblast growth factor receptors) are the receptors that bind to members of the fibroblast growth factor family of proteins. The fibroblast growth factor family constitutes one of the most important groups of paracrine factors that act during development. They are responsible for determining certain cells to become mesoderm, for the production of blood vessels, for limb outgrowth, and for the growth and differentiation of numerous cell types. VEGFRs consist of three subtypes, the fms-like tyrosine kinase Flt-1 (VEGFR1/Flt-1), the kinase domain region, also referred to as fetal liver kinase (VEGFR2/KDR/Flk-1), and Flt-4 (VEGFR3). The VEGF family members VEGF-A, -B, -C, -D, -E, and PlGF, and the human immunodeficiency (HIV) Tat protein bind in specific patterns to three related receptor protein tyrosine kinases, VEGFR1, 2, and 3, and induce the formation of homo- and heteromeric receptor complexes. Binding of VEGF to VEGFR causes dimerization and autophosphorylation of the receptor.
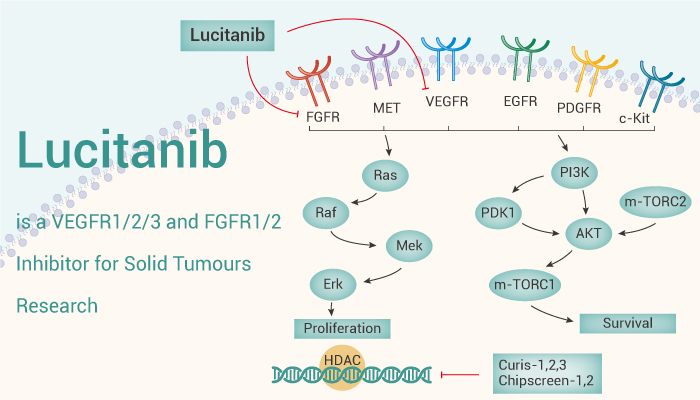
Lucitanib (E-3810) is a novel dual inhibitor of VEGFR and FGFR.
Lucitanib potently and selectively inhibits VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, FGFR1 and FGFR2. Consistent with the inhibitory activity of VEGFR and FGFR auto-phosphorylation, Lucitanib potently inhibits VEGF and bFGF-stimulated HUVEC proliferation. Besides, Lucitanib also inhibits CSF-1R. Lucitanib, at oral dosing of 20 mg/kg for 7 consecutive days, completely inhibits the bFGF induced angiogenic response compare with the response in vehicle-treated mice. Lucitanib shows a broad spectrum of activity, being active in HT29 colon carcinoma, A2780 ovarian carcinoma, A498, SN12K1, and RXF393 renal carcinomas xenografts with dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth. E-3810 significantly delays growth during treatment, but tumors resume their growth when treatment is suspended. This tumor xenograft is very sensitive to Lucitanib, with complete tumor stabilization lasting throughout the 30-day treatment. As in other tumor models, tumors re-grow after withdrawal of Lucitanib at a rate similar to control tumors.
All in all, Lucitanib is a novel dual inhibitor of VEGFR and FGFR, potently and selectively inhibits VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, FGFR1 and FGFR2.
References:
[1] Shibuya M. Genes Cancer. 2011 Dec;2(12):1097-105.
[2] Bello E, et, al. Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 15;71(4):1396-405.