Malignant melanoma represents the most aggressive and deadliest form of cutaneous cancer. This disease possesses the characteristic of increasing incidence, high metastasis, rapid disease progression, poor prognosis, and high mortality. The latest data showed that patients with metastatic melanoma have a poor prognosis with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. Some targeted agent therapies have recently become available for metastatic melanoma. For instance, BRAF and MEK1/2 inhibitors become monotherapy or combined approaches for mutant melanoma treatment.
However, the clinical benefit of these therapies is limited to the rapid development of resistance. In a few years, immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of melanoma. Antibodies that block the negative co-stimulatory receptors CTLA-4 and PD-1 have been approved based on significantly longer overall survival in clinical trials compared to other therapies. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) participate in the epigenetic regulation of target genes through deacetylating lysine ε-amino groups on histone tails to promote a status of DNA condensation and transcriptional silencing.
In general, broad-spectrum HDAC inhibitors regulate chromosome remodeling, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity in cancer. Additionally, pan-HDACis can upregulate the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in human and murine melanoma cells. Besides, essential concerns regarding the toxicity of pan-HDACis are rising since their broad inhibition may result in unwanted off-target effects that eventually impair their clinical profile. Thus, there is an emerging interest in the development and investigation of selective HDACis to better understand the molecular mechanisms mediating the anti-tumor effects.
SS-208, discovered by Sida Shen, is a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 12 nM. Of course, SS-208 possesses anti-tumor activity in melanoma.
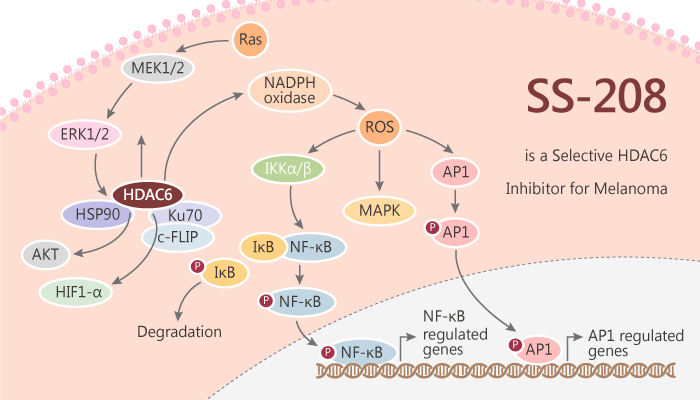
SS-208 exhibits much less potency for other HDAC subtypes, the IC50 values are more than 1 μM.
In vivo, SS-208 (25 mg/kg, IP) significantly reduces the tumor growth in melanoma murine model.
Collective, highly-selective HDAC inhibitors have the potential to be promising candidate drugs for melanoma treatment.