Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) is a kinase. B cells and myeloid cells expressed exclusively. It plays a vital role in B cells. Btk plays an essential role in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway. Antigen binding to the BCR results in B cell receptor oligomerization, Syk and Lyn kinase activation, followed by Btk kinase activation. Once activated, Btk forms a signaling complex with proteins such as BLNK, Lyn, and Syk and phosphorylates phospholipase C (PLC)g2. BCR signaling also contributes to several B cell malignancies, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma, and subsets of diffuse large B cell leukemia. CC-292 is a potent, highly selective, covalent inhibitor of Btk. It inhibits BCR signaling and has efficacy in a rheumatoid arthritis disease model. In this study, CNX-500 is a probe consisting of a covalent Btk inhibitor (CC-292) and chemically links to biotin.
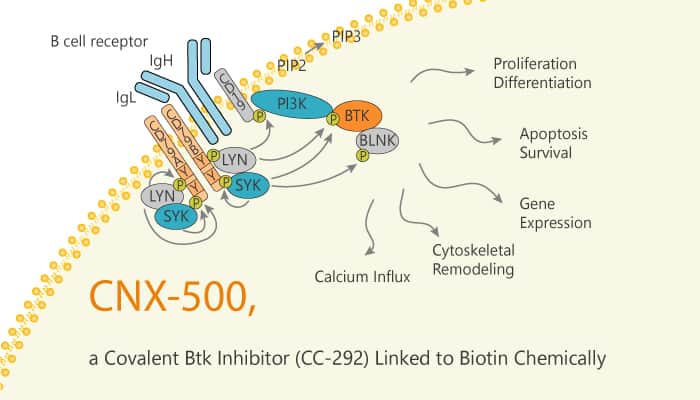
CNX-500 detects free, uninhibited Btk in a competition assay. In Ramos cells exposed to a range of CC-292 concentrations, the amount of Btk captured by the probe and the extent of Btk bonded is proportional to CC-292 drug concentration. In addition, the covalent mechanism of action of CC-292 enabled the design of a companion PD assay. It directly quantifies covalent bonding to Btk protein after drug exposure. Furthermore, it retains inhibitory activity against Btk (IC50app=0.5 nM). CNX-500 also has the ability to form a covalent bond with Btk. CNX-500 selectivity against the structurally related kinase epidermal growth factor receptor, and upstream Src-family kinases including Syk and Lyn.
In summary, CNX-500 is a probe consisting of a covalent Btk inhibitor (CC-292) chemically. More, it retains inhibitory activity against Btk (IC50 of 0.5 nM) and the ability to form a covalent bond with Btk.
Reference:
Evans EK, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Aug;346(2):219-28.