Despite the introduction of new targeted therapies and cytotoxic agents, chemotherapy-pretreated metastatic breast cancer (MBC) remains an essentially incurable disease with only moderate median overall survival (OS). over 20 human tumor types overexpress C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4). CXCR4 levels correlate with aggressive metastatic phenotypes and negative prognosis in breast cancer. Its natural ligand, stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1), is expressed highly at common sites of breast cancer metastases. Disrupting CXCR4-dependent pathways might prevent the development of breast cancer metastases. Balixafortide (POL6326) is a potent, selective, well-tolerated peptidic CXCR4 antagonist with an IC50 < 10 nM. Balixafortide shows 1000-fold selective for CXCR4 than a large panel of receptors including CXCR7.
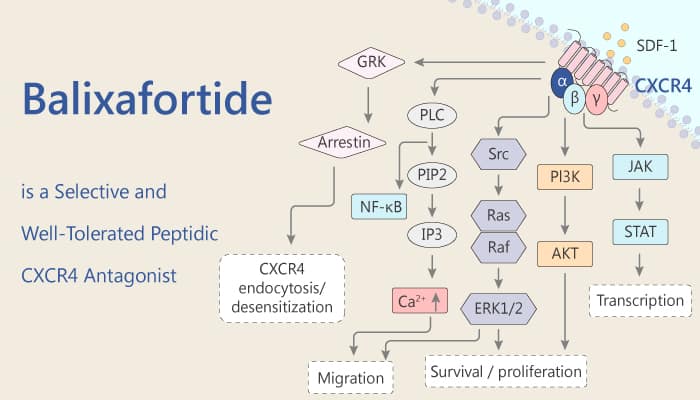
Balixafortide blocks β-arrestin recruitment and calcium flux with IC50s < 10 nM, and it is also a potent hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) mobilizing agent. Moreover, it shows anti-cancer effects. It also potently inhibits pERK/pAKT signaling in the lymphoma lines Namalwa (IC50< 200 nM) and Jurkat (IC50 < 400 nM). Furthermore, Balixafortide efficiently blocks SDF-1 dependent chemotaxis of MDA MB 231 breast cancer cells (IC50 < 20 nM), Namalwa and Jurkat cells (IC50 < 10 nM). Meanwhile, Balixafortide is optimized for favorable mouse absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) properties with balanced plasma protein binding, greater plasma and microsomal stability. In addition, in murine models of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), POL5551 (a balixafortide analogue) + eribulin shows enhanced cytotoxic activity and inhibition of metastases compared with eribulin alone. Therefore, Balixafortide plus eribulin has the potential to provide a new therapeutic option.
In summary, Balixafortide is a potent antagonist of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Disrupting CXCR4 dependent pathways prevents the development of breast cancer metastases, enhances the cytotoxic effect of chemotherapy and immunotherapy, and counteracts tumor cell evasion of the immune system.
Reference:
Zimmermann J, et al. Ann Oncol. 2018 Oct;29 Suppl 8:viii103.
Karpova D, et al. J Transl Med. 2017 Jan 3;15(1):2.