Janus kinases (JAK) play a crucial role in cytokine-mediated signal transduction. Activated JAKs tyrosine autophosphorylate and phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the C-terminal end. This results in the recruitment and activation of the STAT proteins. Activated STATs subsequently translocate into the nucleus where they alter specific gene transcription patterns. The mammalian JAK kinase family comprises four members: JAK1-3 and TYK2.5. JAKs express ubiquitously, except JAK3 primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells. Their constitutive or enhanced activity usually result in a series of hematologic malignancies including lymphoid and myeloid leukemias, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and various B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas.
Studies have demonstrated that JAK2-deficiency is embryonically fatal in mice due to a lack of erythropoesis. As a consequence, no in vivo JAK2 knock out animal model exists, which makes the biological characterization of JAK2 more difficult. JAK2 antagonists, however, could be used efficiently for analyzing the possible therapeutic benefit of JAK2 inhibition in hematologic malignancies and myeloproliferative disorders. On the other hand, there have been only a small number of JAK2 inhibitors.
AG490 possesses significant JAK2 inhibition. AG490 blocks leukemic cell growth significantly both in vitro and in vivo. On the other hand, this compound lacks sufficient target specificity, therefore the interpretation of results obtained with AG490 may not be limited to JAK2 inhibition. Since off-target effects may cause serious immuno-modulative or proliferative side effects, specific JAK2 inhibition is highly desirable.
In the study, scientists identified and verified a compound G6 (NSC 33994) as a JAK2 selective inhibitor.
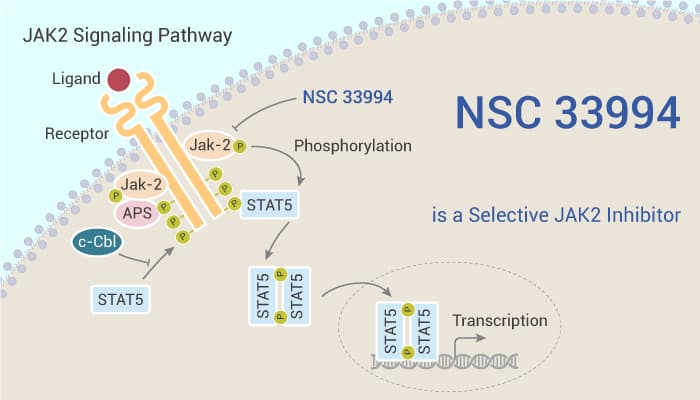
NSC 33994 (G6) reduces the levels of phospho-JAK2 in both a dose- and time-dependent manner.
NSC 33994 (G6, 0-25 μM, 0-48 h) inhibits phospho-JAK2 (pY1007/pY1008) in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner.