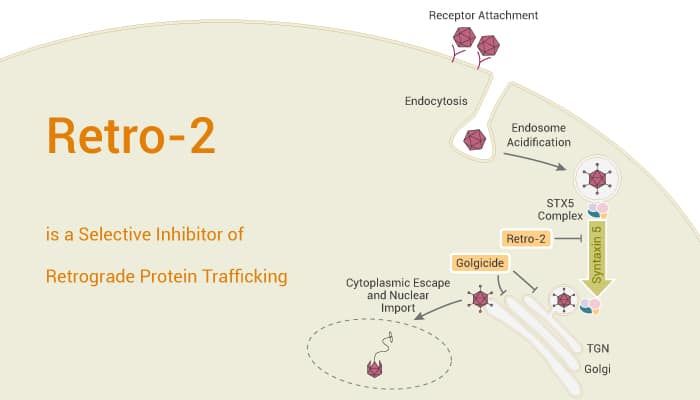
Viruses critically depend on host cellular factors to establish a productive infection. Retro-2 is an inhibitor of endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport of the plant toxin ricin and bacterial Shiga toxin. However, the efficacy of Retro-2 also has been examined against enveloped viruses, such as filoviruses.
As a result, Retro-2 is an ebolavirus (EBOV) infection inhibitor. It shows an EC50 of 12.2 µM in HeLa cells. Besides, Pretreatment for 30 min with Retro-2 inhibits HeLa cell intoxication by ricin, Shiga-like toxins 1 (Stx1) and 2 (Stx2).
And, Retro-2 blocks the invasion of cells by the intracellular parasite Leishmania. As well as replication of non-enveloped viruses, including polyoma-, papilloma-, and adeno-associated viruses.
In female Balb/c mice (Pathogen-free 6-week-old) with ricin (2 μg/kg). The dose for Retro-2 is non-toxic for animals even up to 400 mg/kg. After a single dose of 2 mg/kg of Retro-2 injection prior toxin challenge, forty-nine percent of Retro-2-injected mice survive. while in the control group, survival was as low as 11.5%. Finally, 200 mg/kg of Retro-2 fully protected mice against ricin challenge.
Retro-2 selectively inhibits cellular toxin uptake without affecting compartment integrity, endogenous retrograde cargo transport, and a number of other trafficking events.
Autophagy is a catabolic recycling process by a cell degradation to cell homeostasis or survival. Additionally, Retro-2 can induce autophagy in GFP-LC3-expressing HeLa cells. It promotes the dramatic cytoplasmic accumulation of large autophagosomes. It abolishes autolysosome formation.
Furthermore, Retro-2 disassembles the cell MT network and does not affect the cell actin cytoskeleton.
Additionally, Retro-2 treatment shows an increase over time in the abundance of LC3-II protein in cells. Retro-2 acts as a key regulator of vacuolar trafficking of the autophagy pathway.
In conclusion, Retro-2 exerts a broad-spectrum activity against the cellular trafficking of toxins, intracellular bacterial pathogens, and other viruses. And, It acts as a small autophagy-regulating compound under experimental investigation for diverse diseases research, including cancer.
Reference:
[1]. Bahne Stechmann, et al. Cell. 2010 Apr 16;141(2):231-42.
[2]. Valérie Nicolas, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 18;8:464.