RNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Specifically, RNA synthesis or transcription is the process of transcribing DNA nucleotide sequence information into RNA sequence information. Besides, RNA synthesis is catalyzed by a large enzyme called RNA polymerase. The basic biochemistry of RNA synthesis is common in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Ribosomal RNA transcription is the rate-limiting step in bacterial ribosome synthesis. Besides, this information must be transcribed by RNA polymerase and translated by the ribosome before it can reach its final form.
In eukaryotic cells, the task of transcribing nuclear genes is shared by polymerases (Pols) I, II, and III. Furthermore, Pol II produces mRNA encoding cellular proteins and many snRNAs involved in mRNA processing. Pol III synthesizes tRNA, 5S rRNA, and various other small untranslated RNAs that play an important role in metabolism. Meanwhile, Pol I aims to synthesis of rRNA, which accounts for 60% of the transcriptional activity of eukaryotic cells. Pol I-specific transcription factors guide Pol I to the rDNA promoter. It participates in multiple rounds of transcription initiation, promoter escape, extension, and termination. Nonetheless, Pol I transcription dysregulation is a feature of cancer and other diseases characterized by abnormal translation capabilities. Here, we will introduce an oral rRNA synthesis inhibitor, CX-5461.
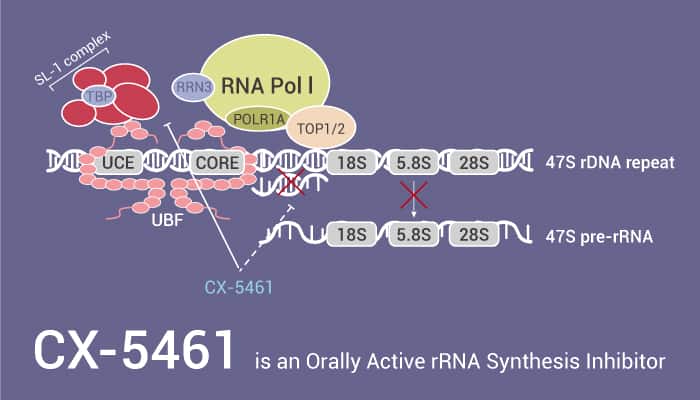
CX-5461 is an Orally Active rRNA Synthesis Inhibitor.
Above all, CX-5461 inhibits RNA Pol I-driven transcription of rRNA with IC50s of 142, 113, and 54 nM in HCT-116, A375, MIA PaCa-2 cells, respectively. Interestingly, CX-5461 shows little or no effect on Pol II (IC50, ≥25 μM). Importantly, CX-5461 has modest inhibition on DNA replication and protein translation. CX-5461 also exhibits broad antiproliferative activity against a panel of human cancer cell lines, with a mean EC50 of 147 nM. Particularly, CX-5461 induces autophagy and senescence in solid tumor cancer cells.
Next, CX-5461 displays antitumor activity against human solid tumors in murine xenograft models. Obviously, CX-5461 with 50 mg/kg by p.o. shows significant MIA PaCa-2 growth inhibition on day 32. CX-5461 inhibits the Eμ-Myc tumor cells with 84% repression in Pol I transcription at 1 hr posttreatment in C57BL/6 mice. Additionally, CX-5461 also induces a rapid reduction in tumor burden in the lymph nodes.
All in all, CX-5461 is a potent and oral rRNA synthesis inhibitor.
References:
Drygin D et al. Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 15;71(4):1418-30.