TRPML1, also known as Mucolipin-1 (transient receptor potential cation channel), is a 65 kDa protein encoded by the MCOLN1 gene in humans associated with mucolipidosis type IV. As a non-selective cation channel, TRPML1 can guide iron ions through the endosome/lysosomal membrane into cells, and the mutation or deletion of TRPML1 may lead to iron deficiency in cells. TRPML1 is also a major calcium release channel on lysosomal membranes. Also, it plays an important role in lysosomal signaling during nutrient deprivation. Lysosomal calcium release by TRPML1 promotes dephosphorylation of TFEB by the phosphatase calcineurin, thereby inducing TFEB nuclear translocation and subsequent transcriptional activation of lysosomal and autophagy genes. TRPML1 is a multi-step regulator of autophagy, which can be used to treat LSD and other autophagic diseases, etc.
ML-SA5 is a Potent TRPML1 Cation Channel Agonist.
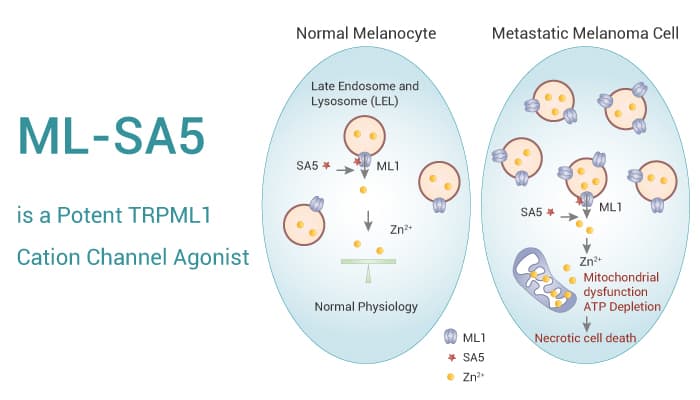
ML-SA5 is a potent TRPML1 cation channel agonist that activates the entire endosomal TRPML1 (ML1) current in DMD myocytes with an EC50 of 285 nM. Moreover, ML-SA5 is more potent than ML-SA1. ML-SA5 has anticancer activity and can tumor growth. In vitro studies have shown that ML-SA5(1-100 μM, 24 h) has some cell-targeting specificity and induces substantial cell death in M12 and MeWo cells. But it fully preserves normal melanocytes. It also causes a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in M12 cells. In some in vivo studies, ML-SA5 (i.p., 2-5 mg/kg, daily, 2 weeks) reduces muscle necrosis in MDX mice by more than 70% and reduces centrally nucleated fibers. This shows that ML-SA5 can improve muscle atrophy in mdx mice in vivo by promoting myosin repair. However, it has no effect in ML1 knockout mice. Moreover, ML-SA5 reduces skeletal and cardiac muscle damage in mdx mice through ML1 upregulation.
In conclusion, ML-SA5 is a potent TRPML1 agonist with some anticancer activity.
Reference:
[1] Wanlu Du, et al. Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 19;37(3):109848.
[2] Lu Yu, et al. Sci Adv. 2020 Feb 7;6(6):eaaz2736.