Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD). Hence, the characteristics of IPF is self-sustaining fibrosis, deteriorating lung function, worsening symptoms (e.g. dyspnoea, cough), increasingly impaired health-related quality of life (HR-QOL) and premature mortality. However, the median survival from the time of diagnosis is 4.5 years. In fact, research shows that the fibroblast growth factor (FGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases have proved to be valuable therapeutic targets in the treatment of IPF, with FGF, PDGF and VEGF mediating profibrotic processes and being implicated in IPF pathogenesis. Therefore, we will introduce a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and Triple Angiokinase inhibitor-Nintedanib (BIBF 1120).
Nintedanib is an orally active tyrosine kinase/triple angiokinase inhibitor.
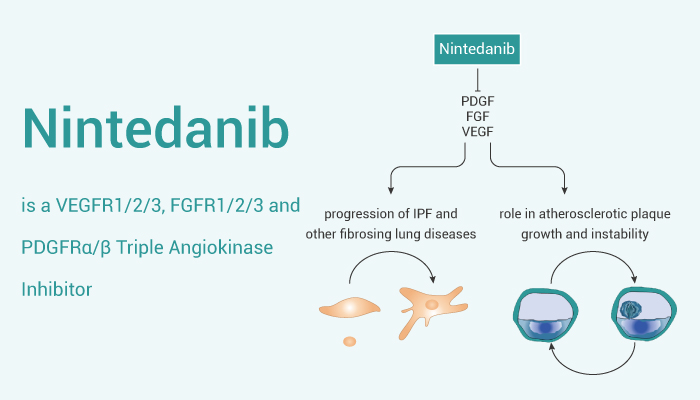
In addition, Nintedanib with IC50s of 34/13/13 nM, 69/37/108 nM and 59/65 nM for VEGFR1/2/3, FGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β, respectively. Moreover, Nintedanib developed as an antitumor agent initially, and with antifibrotic properties.
Firstly, in vitro experiments, Nintedanib binds to the ATP-binding site in the cleft between the amino and carboxy terminal lobes of the kinase domain. Moreover, Nintedanib inhibits proliferation of PDGF-BB stimulated BRPs with EC50 of 79 nM in cell assays. In addition, Nintedanib (100 nM) blocks activation of MAPK after stimulation with 5% serum plus PDGF-BB.
In addition, when in vivo experiments, Nintedanib (3, 10, 30, 100 mg/kg; p.o.; single) inhibits PDGF-BB stimulated PDGFR phosphorylation in mouse lung tissue. In addition, Nintedanib (pretreat; 30, 60 mg/kg; p.o.; single daily for 14 days) reduces bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis. Moreover, Nintedanib (25-100 mg/kg; p.o.; single daily) is highly active in tumor models, including human tumor xenografts growing in nude mice and a syngeneic rat tumor model.
All in all, Nintedanib is a potent tyrosine kinase/triple angiokinase inhibitor, which can be used in study of IPF and cancer.
Reference:
[1] Hilberg F, et al. Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 15;68(12):4774-82.
[2] Roth GJ, et al. J Med Chem. 2009 Jul 23;52(14):4466-80.
[3] Wollin L, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 May;349(2):209-20.
[4] Lamb YN. Drugs. 2021 Apr;81(5):575-586.