c-Met is a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in embryogenesis, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. Abnormal activation of the MET signaling pathway promotes the growth, survival, migration and invasion of tumor cells in various tumors. Therefore, High levels of MET amplification and mutations influence treatment decisions in NSCLC. And c-Met inhibiton can effectively target it. However, there are four biomarkers commonly used clinically to indicate Met inhibitory response: IL-8, GROα and soluble form uPAR. This information can help monitor the development of MET-amplified solid tumors. At the same time, c-Met is also a novel, highly conserved adipogenic mediator that regulates lipid accumulation in mouse adipocytes. c-Met inhibition can strongly reduce lipid accumulation and is a potential key point in the anti-obesity mechanism. Here we introduce an effective c-Me inhibitor, JNJ-38877605.
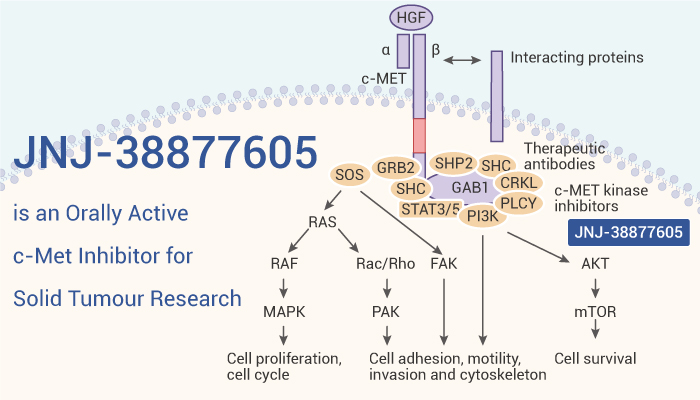
JNJ38877605 is a c-Met inhibitor with anti-tumor activity.
Firstly, JNJ-38877605 is an orally active, ATP-competitive c-Met inhibitor with IC50=4 nM. It is highly selective for c-Met, 600-fold over 200 other tyrosine and serine-threonine kinases. And then, JNJ-38877605 has no significant cytotoxicity. Moreover, it inhibits MET phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, reducing lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) content.
In vivo experiments, JNJ-38877605 (50 mg/kg, po, qd for 13 days) inhibits ionizing radiation (IR)-induced invasion and promotes apoptosis in the U251 xenograft tumor model. (40 mg/kg, po, qd for 3 days) also decreases the plasma concentrations of IL8, GROa, and uPAR in the Met-dependent GTL16 gastric cancer tumor xenograft mouse model, indicating that c-Met was effectively inhibited.
In summary, JNJ-38877605 is an orally effective c-Met inhibitor. It inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and regulates lipid accumulation and can be used in tumor and metabolic disease research.
References:
[1] De Bacco F, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 Apr, 103(8), 645-661.
[2] Torti D, et al. Int J Cancer. 2012, 130(6), 1357-1366.
[3] Park YK, et.al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 29;24(9):8086.