CXCRs (CXC chemokine receptors) are integral membrane proteins that specifically bind and respond to cytokines of the CXC chemokine family. There are seven CXC chemokine receptors in mammals, named CXCR1 through CXCR7. Among chemokine receptors, CXCR4 is the most widely expressed, and is involved in numerous physiological and pathological conditions. CXCR4 is expressed by most cells, including hematopoietic and endothelial cells (ECs), neurons and stem cells (embryonic and adult). Increased levels of CXCR4 are present in cancer cells.
CXCR4 is a 352 amino acid rhodopsin-like GPCR, comprising an extracellular N-terminal domain, 7 transmembrane helices, 3 extra-cellular loops, 3 intra-cellular loops and an intracellular C-terminal domain. The canonical ligand of CXCR4 is CXCL12, also known as SDF-1. CXCL12 only binds to chemokine receptors CXCR4 and ACKR3, itself a CXCR4 interactor. HMGB1 is the archetypal DAMP molecule. HMGB1 can form a heterocomplex with CXCL12 that also binds to CXCR4. CXCR4 also binds macrophage MIF, a cytokine involved in the regulation of innate immunity. CXCR4 and CXCL12 can control the regeneration of multiple organs and tissues, including lung, heart, liver, and the nervous system.
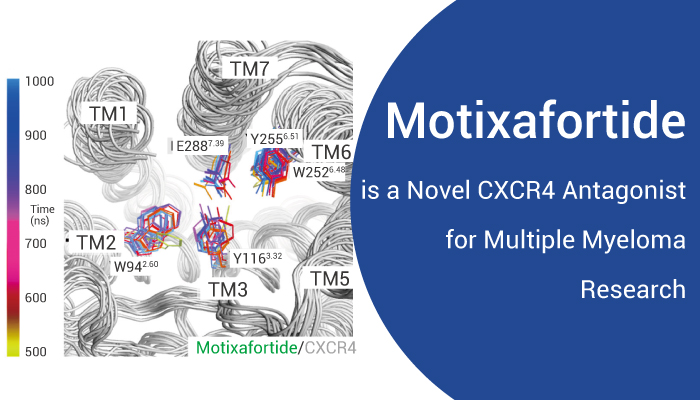
Motixafortide (BKT140 4-fluorobenzoyl) is a selective cyclic-peptide inhibitor of CXCR4
Motixafortide exhibits high affinity and slow receptor dissociation rate. Motixafortide is a cyclic peptide hematopoietic stem cell mobilizer that can improve stem cell collection prior to autologous transplantation. In vitro, Motixafortide displays selective toxicity toward acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma (MM) cells. Besides, Motixafortide can overcome IL-6 dependent proliferation and survival of ARH77 MM cells. Moreover, Motixafortide specifically triggers CXCR4-dependent cell death in leukemia and MM cells. Meanwhile, Motixafortide stimulates apoptotic cell death in leukemia and MM cells. In vivo, Subcutaneous injections of Motixafortide significantly reduces the growth of human acute myeloid leukemia and MM xenografts. Besides, tumors from animals treated with Motixafortide are smaller in size and weights, had larger necrotic areas and high apoptotic scores.
All in all, Motixafortide is a potent and selective antagonist of CXCR4 for cancer research.
References:
[1] Bianchi ME, et, al. Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 28:11:2109.
[2] Crees ZD, et, al. Nat Med. 2023 Apr;29(4):869-879.