Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL; henceforth referred to as CLL) are CD5-positive lymphoproliferative neoplasms. It characterized by the clonal proliferation and accumulation of mature B cells in the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes and spleen.
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with CLL/SLL or relapsed/refractory MCL. Acalabrutinib is a highly selective, next-generation BTK inhibitor. In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration approval Acalabrutinib for the treatment of adult patients with MCL.
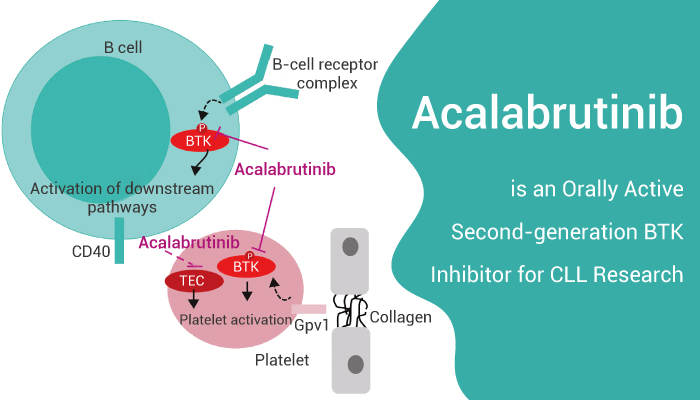
Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) is an orally active, irreversible, and highly selective second-generation BTK inhibitor.
First, Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of downstream targets of ERK, IKB, and AKT, in the in vitro signaling assay on primary human CLL cells. Second, In the human CLL NSG xenograft model, Acalabrutinib demonstrates on-target effects including decreased phosphorylation of PLCγ2, ERK and significant inhibition of CLL cell proliferation. Third, Acalabrutinib inhibits purified BTK with an IC50 of 3 nM and an EC50 of 8 nM in a human whole-blood CD69 B cell activation assay. Acalabrutinib has improved target specificity over ibrutinib with 323-, 94-, 19-, and 9-fold selectivity over the other TEC kinase family members (ITK, TXK, BMX, and TEC, respectively) and no activity against EGFR.
In vivo, Acalabrutinib demonstrates potent on-target effects and efficacy in mouse models of CLL. It (100 mg twice per day) exhibits more selective for inhibiting BTK at injured arterioles of the mice.
Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) is an orally active, irreversible, and highly selective second-generation BTK inhibitor for the research of CLL.
Reference:
[1] Danilov AV, et al. Br J Haematol. 2021 Apr;193(1):15-25.
[2] Wu J, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Mar 9;9:21.
[3] Herman SEM, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 1;23(11):2831-2841.