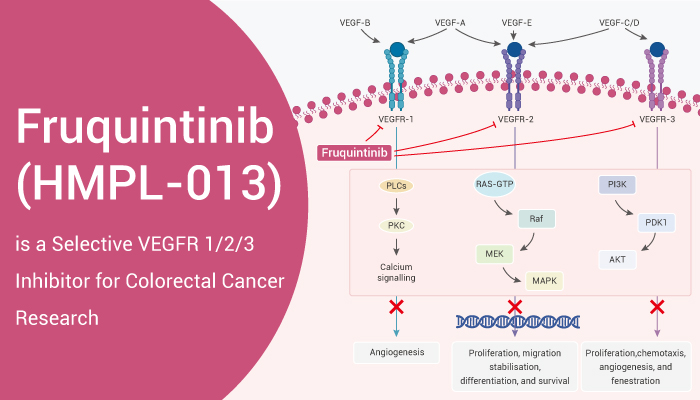
VEGF receptor (VEGFR) is the receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR VEGFR 1/2/3. By alternative splicing modification, membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR) forms are further generated. Phosphorylation of the intracellular VEGFR kinase domain triggers downstream cell signaling cascades, including the PI3K/AKT, PKC, Raf/Ras, and ERK pathways, leading to vascular/lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation and the formation of new blood vessel branches. Small molecule inhibitors of VEGFR have been used to inhibit advanced colorectal cancer (CRC). However, most are limited by intravenous administration, immunogenicity, and long-term treatment-induced autoimmune diseases. Here we introduce an orally effective small molecule VEGFR inhibitor, Fruquintinib. It enables sustained target inhibition and can be used in combination with chemotherapy drugs to avoid antibody limitations.
Fruquintinib (HMPL-013) is a potent and selective VEGFR 1/2/3 inhibitor with IC50 values of 33, 0.5, and 35 nM, respectively.
Fruquintinib inhibits VEGF-A-dependent KDR phosphorylation and VEGF-A-induced primary HUVEC proliferation in HEK293-KDR cells with IC50s of 0.6 nM and 1.7 nM, respectively. It also inhibits VEGF-C-stimulated VEGFR3 phosphorylation and cell proliferation in primary HLECs with IC50s of 1.5 nM and 4.2 nM, respectively. And also inhibits tube branching, tube length, and area in a concentration-dependent manner. The tubule length of primary HUVECs is reduced by 74% and 94% at 0.03 and 0.3 μM Fruquintinib, respectively. Fruquintinib inhibits human venous endothelial cell (HUVEC) tubule growth and chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) angiogenesis.
Fruquintinib exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic profiles in multiple animal models. In the gastric cancer BGC-823 model, Fruquintinib inhibits tumor growth at doses of 0.5 and 2 mg/kg (once daily), with inhibition rates of 62.3% and 95.4-98.6%, respectively. When the dose increases to 5 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, tumor regression rates is 24.1% and 48.6%, respectively. The level of anti-tumor growth activity of Fruquintinib varies in different tumor xenograft models. Fruquintinib significantly reduces microvessel density even at the lowest dose of 0.8 mg/kg.
In summary, Fruquintinib is an orally available VEGFR inhibitor that effectively inhibits angiogenesis and progression in gastric cancer models.
Reference:
[1] Sun Q, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1635-45.