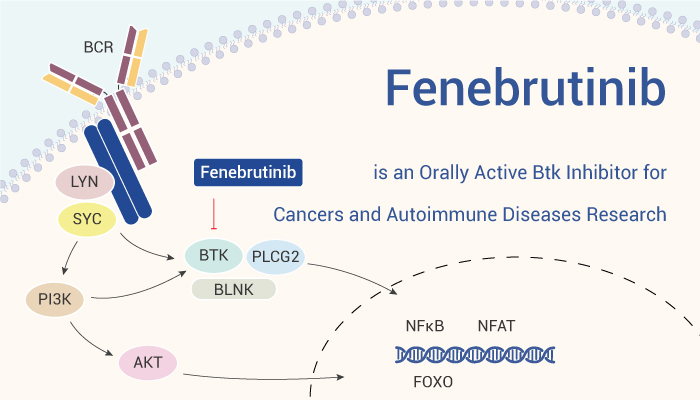
BTK is a member of the Tec family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases involved in B cell and myeloid cell signaling. BTK is located downstream of B cells and Fcγ receptors. Overactivation of BTK causes B cells and myeloid cells to induce or sustain excessive autoimmune responses, such as in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. BTK inhibitors block BCR and Fcγ receptor signaling and inhibit pathogenic immune cell-driven inflammatory or autoimmune diseases. Here we introduce an orally effective BTK inhibitor, Fenebrutinib (GDC-0853).
Fenebrutinib inhibits BTK with a long-lasting, highly selective, non-covalent inhibition mode.
Fenebrutinib inhibits CD69 expression on CD19+ B cells in human whole blood with an IC50 of 8.4 nM. And it inhibits CD63 expression on basophils with IC50=30.7nM. Fenebrutinib also inhibits anti-IgM-induced BTKY223 autophosphorylation in human whole blood (IC50=11 nM). Moreover, it exhibits dose-dependent activity in an in vivo rat model of inflammatory arthritis. Fenebrutinib dose-dependently reduces the development of collagen-induced arthritis in the ankles of female Lewis rats after administration once (4 and 16 mg/kg; p.o.) or twice daily (0.125, 0.5, and 2 mg/kg; p.o.). The half-lives (t1/2) of Fenebrutinib (0.2 mg/kg i.v. and 1.0 mg/kg p.o.; rat) and (0.2 mg/kg i.v. and 0.5 mg/kg p.o.; dog) in rats and dogs are 2.2 and 3.8 h, respectively. However, prolonged administration of Fenebrutinib, results in pancreatic pathology, including multifocal islet central hemorrhage, inflammation, fibrosis, and atrophy, degeneration, and inflammation of pigment-rich macrophage cells adjacent to lobular exocrine acini.
In summary, Fenebrutinib is an orally available BTK inhibitor with antitumor activity, but also exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in inflammatory arthritis models. Can be used in research on rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
References:
[1]. Erickson RI , et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Jan;360(1):226-238.
[2]. Crawford JJ, et al. J Med Chem. 2018 Mar 22;61(6):2227-2245.