Hydroxyurea, also known as hydroxycarbamide, is a straightforward compound. The compound boasts a molecular formula of CH4N2O2. Intriguingly, it bears a structural resemblance to urea. Pioneers first synthesized this compound back in 1869. Hydroxyurea exists primarily as keto form, which provides stability. On the other hand, it has an unstable imino form too. Interestingly, we classify Hydroxyurea as a weak acid. It comes with a pKa value of 10.6. As a nonalkylating antineoplastic agent, Hydroxyurea sees wide use. Health practitioners employ it for hematological malignancies, infectious diseases, and skin disorders.
Researchers discovered its anticancer potential in the late 1950s. This revelation came during experiments involving L1210 leukemia cells and solid tumors. Consequently, in the swinging 1960s, they conducted clinical trials. These investigations confirmed Hydroxyurea’s power against myeloproliferative disorders.
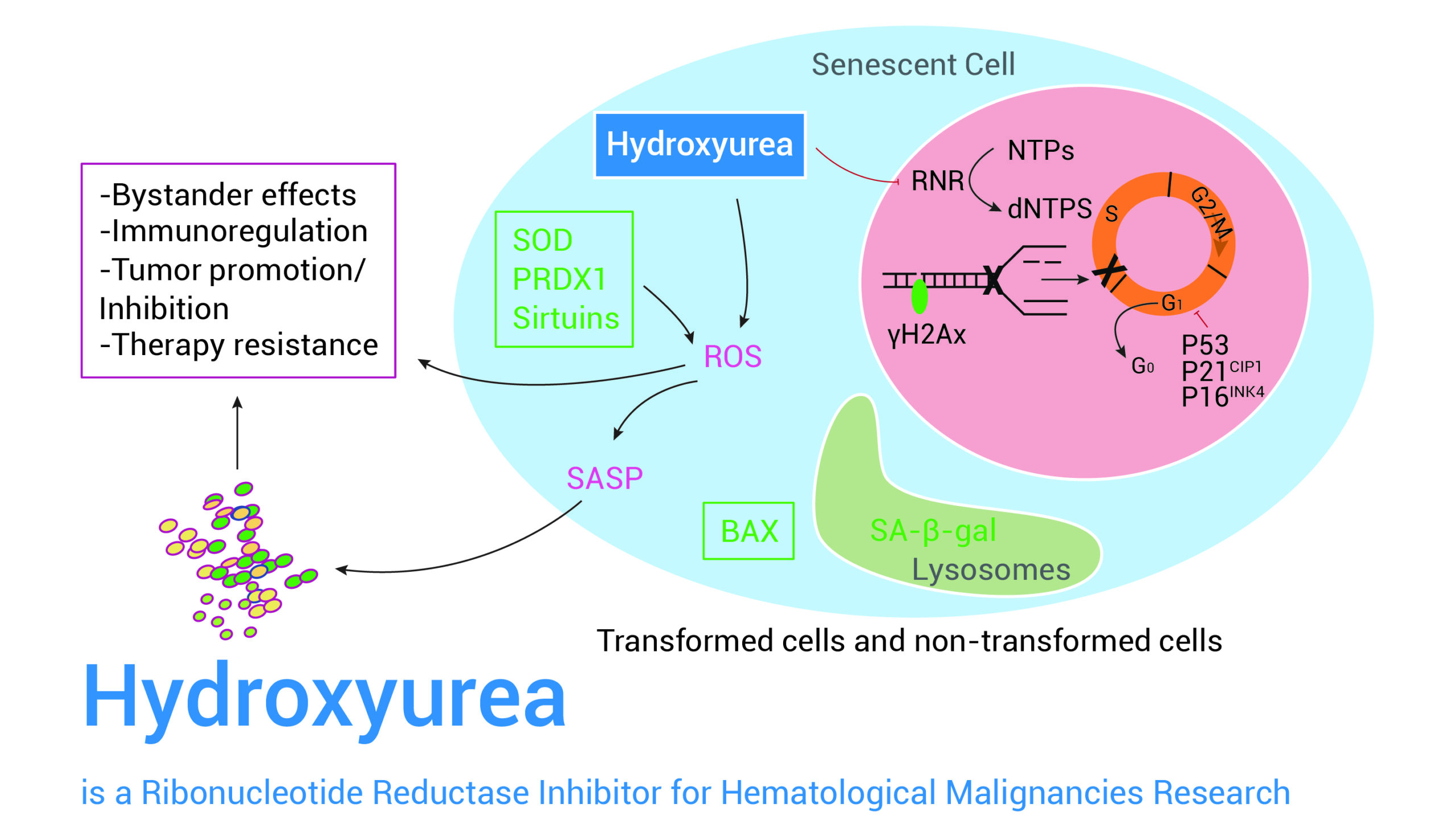
Hydroxyurea is a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor for hematological malignancies research
Hydroxyurea is a remarkable compound that works by triggering cell apoptosis and interrupting DNA synthesis. This interaction happens via the inhibition of an enzyme known as ribonucleotide reductase. Interestingly, research shows that Hydroxyurea also acts against orthopoxvirus.
Furthermore, it’s noteworthy that Hydroxyurea has found extensive applications in treating various diseases. These range from myeloproliferative and neoplastic conditions to HIV and other non-hematological diseases. Intriguingly, experiments involving primary culture cells treated with 30 μM Hydroxyurea for 96 hours have shown significant increases in the fractional HbF content. Additionally, there is an observable increment in the Gγ: Aγ-globin mRNA ranging from 0.30- to 8-fold under in vitro conditions. Moreover, Hydroxyurea has proven efficacy in blocking HIV-1 reverse transcription and replication in certain types of cells, including quiescent peripheral blood mononuclear cells and macrophages.
Nonetheless, it’s crucial to note that Hydroxyurea therapy does not always yield fully positive results. Although it consistently reduces white blood cell (WBC) and absolute neutrophil count (ANC), it reportedly fails to improve anemia over a period of 17 weeks. Studies using sickle cell mice and treating them with 50mg/kg Hydroxyurea resulted in reduced WBC and ANC but no noticeable improvement in their anemia condition compared to those treated with vehicle.
Reference:
[1] Kovacic P. Med Hypotheses. 2011 Jan;76(1):24-31.
[2] Kapor S, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 18;2021:7753857.