The hypoxic bone-marrow (BM) microenvironment confers growth/survival and drug-resistance in myeloma. Novel therapies via targeting hypoxic-BM milieu may overcome drug resistance. A study from Deepika Sharma Das reported a hypoxia-selective epigenetic agent, RRx-001.
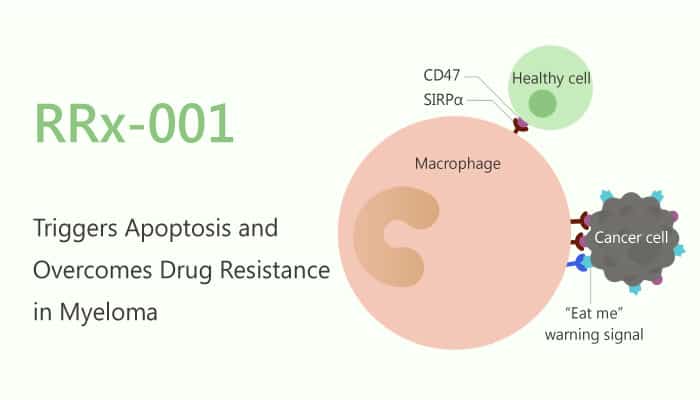
In this study, RRx-001 decreases the viability of MM cell lines, as well as overcomes drug-resistance. Especially, RRx-001 induced apoptosis is associated with activation of caspases, the release of ROS and nitrogen-species, induction of DNA damage via ATM/γ-H2AX, and decrease in DNA methyltransferase. Besides, RRx-001 plus USP7 inhibitor P5091 triggered synergistic anti-MM activity. RRx-001 is also well-tolerated in vivo, inhibits tumor growth, and enhances survival.
In vitro, RRx-001 (0-5 μM, 24 hours) inhibits MM cells growth and overcomes resistance to novel and conventional therapies. It induced a dose-dependent significant (p < 0.05) decrease in the viability of all cell lines.
RRx-001 blocks the migration of MM cells and associated angiogenesis.
Equally, RRx-001 induces significant G1 phase growth arrest, with a concomitant decrease in S phase. RRx-001 triggers significant apoptosis in MM cells.
RRx-001 inhibits DNA methylation by downregulating DNA methyltransferases.
In vivo, RRx-001 (5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg, I.V., thrice-weekly for 24 days) inhibits tumor growth and prolongs survival in a xenograft mouse model.
RRx-001 (10 mg/kg, IP, twice a week and once a day) exhibits potent anti-cancer activity on the A549 lung cancer model dependent on the presence of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor tissue. Moreover, treatment exhibited no apparent weight loss.