Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is primary liver cancer and the third most common cause of cancer mortality worldwide. CGS 15943 blocks proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and pancreatic cancer adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Researchers test the adenosine A2 receptor antagonist CGS 15943 for cerebroprotective activity in a gerbil stroke model.
CGS 15943 displays marked adenosine A2 selectivity in peripheral tissues although it is somewhat less selective for rat brain striatal membranes. Importantly, CGS 15943 targets specifically the catalytic subunit of the class IB PI3K isoform (p110γ). Moreover, CGS 15943 (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) markedly reduces stroke injury assessed by locomotor activity monitoring and by histopathological measurement of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell injury.
CGS 15943 selectively targets p110γ indicating that it may represent a vital lead compound to develop drugs that can specifically target this PI3K isoform whose key role in cancer progression is emerging. CGS 15943 reduces the phosphorylation of Akt at its residues Ser473 and Thr308 in HLF and Sk-Hep-1. Similarly, CGS 15943 inhibits Akt Ser473 phosphorylation in HepG2 cells and in PLC-PRF-5. CGS 15943 inhibits the kinase activity of the class IB PI3K isoform p110γ with an IC50 of 1.1 μM. Researchers also detected a slight inhibition of the class IA PI3K isoform p110δ with an IC50 of 8.47 μM. CGS 15943 can directly inhibit the lipid kinase activity of p110γ.
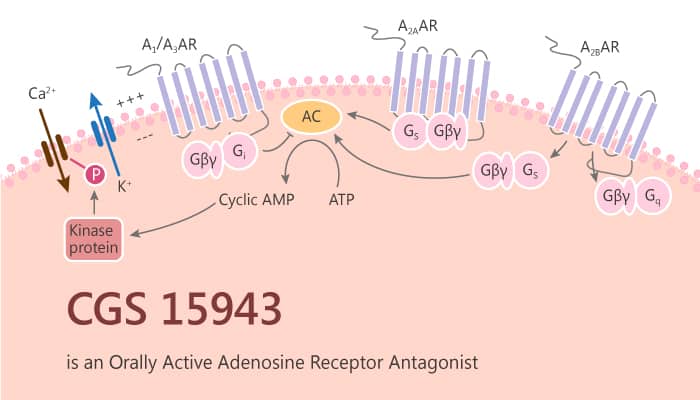
All in all, CGS 15943 is a nonselective antagonist with Ki values in the low nanomolar range for adenosine A1 and A2A receptors and an approximately tenfold lower potency at the adenosine A2B and A3 subtypes.
Reference: