The chimeric proteolytic enzyme (PROTAC) is a heterobifunctional small molecule. Specifically, it is composed of two active domains and an adaptor that can remove specific proteins that are not needed. Besides, PROTAC does not act as a conventional enzyme inhibitor, but by inducing selective intracellular proteolysis. Moreover, PROTAC includes two covalently linked protein binding molecules: one can bind E3 ubiquitin ligases, the other can bind to the target protein to be degraded. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) participates in the regulation of transcription, mRNA processing, and differentiation of nerve cells. Furthermore, CDK4/6 induces the G1-S cell cycle transition by phosphorylation of tumor, which triggers the expression process of gene Promoting S phase entry. Therefore, CDK4/6 is an attractive target for cancer treatment. Current CDK4/6 inhibitors target their highly conserved ATP binding pockets. BSJ-03-204 is a potent and selective Palbociclib-based CDK4/6 dual degrader (PROTAC).
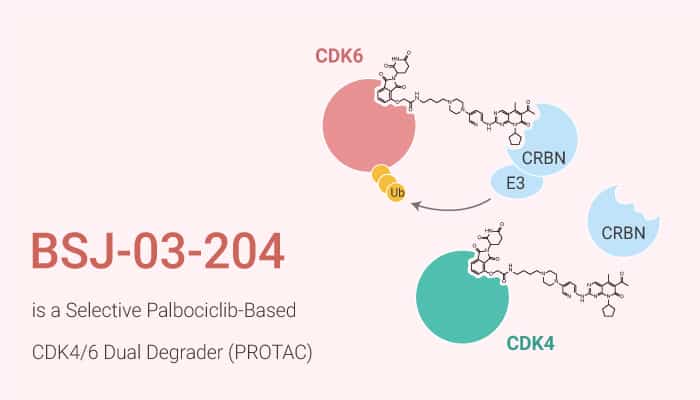
BSJ-03-204 is a potent and selective Palbociclib-based CDK4/6 dual degrader (PROTAC).
But, how does BSJ-03-204 protect against cancer cells via CDK4/6? Let’s discuss it in detail. First of all, BSJ-03-204 is a selective Palbociclib-based CDK4/6 dual degrader (PROTAC), with IC50s of 26.9 nM and 10.4 nM for CDK4/D1 and CDK6/D1, respectively. Meanwhile, BSJ-03-204 does not induce IKZF1/3 degradation and has anti-cancer activity.
In the second place, BSJ-03-204 with 0.0001-100 μM has potent anti-proliferative effects on MCL cell lines for 3 or 4 days. Importantly, BSJ-03-204 potently induces a G1 arrest with 1 μM for 1 day. Particularly, BSJ-03-204 only results in the degradation of CDK4/6 in WT cells, not IKZF1/3 with 0.1-5 μM for 4 hours.
All in all, BSJ-03-204 is a potent and selective Palbociclib-based CDK4/6 dual degrader (PROTAC).
References:
Baishan Jiang, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 May 6;58(19):6321-6326.