BCL-XL is a member of the Bcl-2 protein family and a transmembrane molecule in mitochondria. Specifically, it acts as an anti-apoptotic protein by blocking the release of mitochondrial contents such as cytochrome c. Besides, BCL-XL is a well-validated cancer target and eventually leads to caspase activation and eventually programmed cell death. Moreover, small-molecule inhibition of Bcl-2 family proteins has been widely used in cancer treatment strategies. Furthermore, PROTAC is a small bivalent molecule containing ligands that recognize the target protein linked to the E3 ligase ligand. Such molecules can recruit the target protein to E3 ligase, promote the adjacent induced ubiquitination of the target protein. And they cause its degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). Meanwhile, PROTAC technology can reduce thrombocytopenia induced by BCL-XL inhibition. DT2216 is a potent and selective BCL-XL degrader based on PROTAC technology.
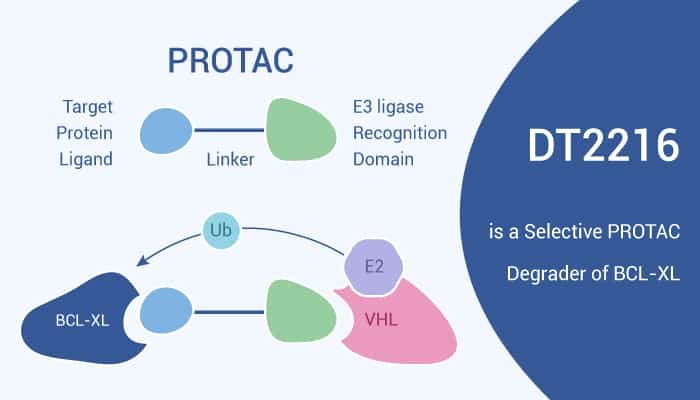
DT2216 is a potent and selective BCL-XL degrader based on PROTAC technology.
But, how does DT2216 protect against cancer cells via BCL-XL? Let’s discuss it in detail. First of all, SIAIS178 causes effective degradation of BCL-XL protein by recruiting Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nonetheless, DT2216 inhibits various BCL-XL-dependent leukemia and cancer cells but considerably less toxic to platelets.
In the second place, DT2216 with 62.5, 125 nM by 72 hours kills MOLT-4 cells. Particularly, DT2216 shows highly toxic to MOLT-4 cells with an EC50 of 0.052 μM. Obviously, DT2216 kills MOLT-4 cells by caspase-3-mediated induction of apoptosis in a BCL-2 homologous antagonist killer (BAK)- and BCL-2-associated X protein (BAX)-dependent manner.
Last but not the least, DT2216 of 15 mg/kg is more effective at suppressing the growth of MOLT-4 T-ALL xenografts in mice than 7.5 mg/kg by i.p. for 60 days.
All in all, DT2216 is a potent and selective BCL-XL degrader based on PROTAC technology.
References:
Khan S, et al. Nat Med. 2019 Dec;25(12):1938-1947.