Genotoxic antitumor drugs cause DNA damage and activate cell cycle checkpoints, which are required for DNA repair and the maintenance of genomic integrity. The transcription factor p53 is a critical checkpoint protein. As a result, in the presence of damaged DNA, p53 stabilized and activated, causes the upregulation of the CDK inhibitor p21,. Interestingly, p21 induces a subsequent delay in the cell cycle to facilitate DNA repair and/or apoptosis. The main proximal kinases are the PI3K homologs ATM and ATR. More recently, inhibition of CHK1 function ave confirmed these early observations. Consequently, the development of CHK1 inhibitors and the characterization of suitable biomarkers have become an important drug development objective.
Scientists present the preclinical pharmacology and therapeutic utility of SAR-020106, a novel, selective, and potent inhibitor of CHK1.
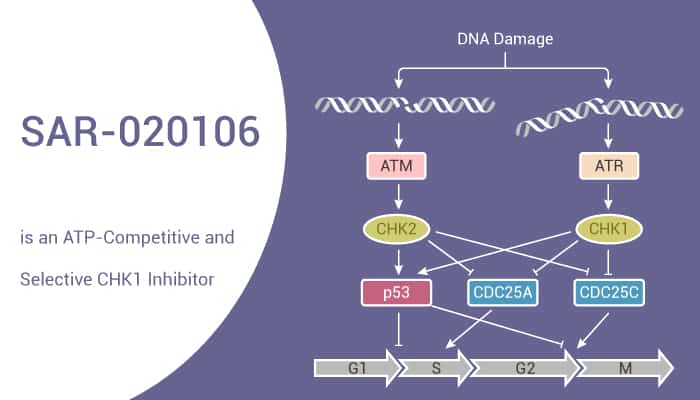
In addition, SAR-020106 is an ATP-competitive, potent, and selective CHK1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 13.3 nM for human CHK1. And it shows excellent selectivity over CHK2. SAR-020106 significantly enhances the cell killing of Gemcitabine and SN38 by 3- to 29-fold in several colon tumor lines and in a p53-dependent fashion. The inhibitor can enhance antitumor activity with selected anticancer drugs.
Besides, SAR-020106 (0.1-1 μM; 23 hours) abrogates an Etoposide-induced S and G2 arrest.
SAR-020106 abrogates Etoposide-induced cell cycle arrest with IC50s of 55 nM and 91 nM in HT29 and SW620 cells, respectively. Additionally, SAR-020106 is relatively nontoxic with a GI50 of 0.48 μM in HT29 and 2 μM in SW620, resulting in an activity index of 8.7 and 22, respectively. What’s more, SAR-020106 inhibits cytotoxic drug-induced autophosphorylation of CHK1 at S296 and blocks the phosphorylation of CDK1 at Y15 in a dose-dependent fashion.
Moreover, SAR-020106 (40 mg/kg; i.p., administered on days 0, 1, 7, 8, 14, and 15) in combination with Irinotecan potentiates the antitumor activity in SW620 xenografts.
Reference: