Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Members of the ERBB receptor tyrosine kinase family include EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4. They present an attractive option for targeted therapy in patients with NSCLC, due to observed patterns of oncogenic mutation of EGFR and HER2. In addition, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the eighth most common cancer worldwide. EGFR is often overexpressed in esophageal cancers, thus anti-EGFR inhibitors have been evaluated in ESCC. In this study, Aatinib potently suppresses the kinase activity of wild-type and activated EGFR and HER2 mutants. In addition, Aatinib can inhibit cell proliferation effectively by arresting the cells in G0/G1 phase. Moreover, it induces apoptosis in ESCC. Thus, Afatinib is an irreversible EGFR family inhibitor. The IC50s are 0.5 nM, 0.4 nM, 10 nM, and 14 nM for EGFR wt, EGFR L858R, EGFR L858R/T790M, and HER2, respectively.
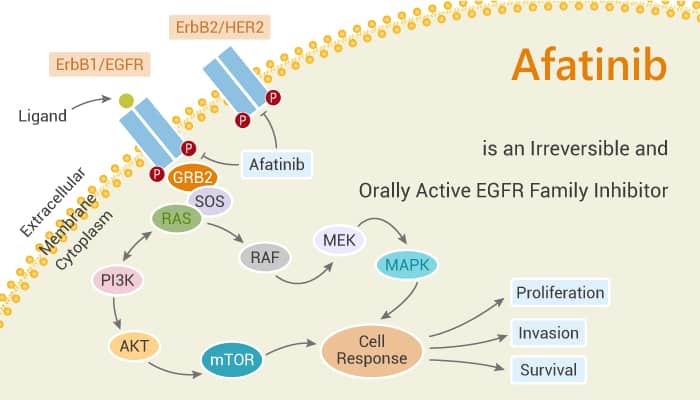
In cell-free in vitro kinase assays, Afatinib shows potent activity against wild-type and mutant forms of EGFR and HER2. It is similar to Gefitinib in potency for L858R EGFR. However, Afatinib shows about 100-fold more activity against the Gefitinib-resistant L858R-T790M EGFR double mutant, with an IC50 of 10 nM. Afatinib is furthermore comparable to Lapatinib and Canertinib for in vitro potency against HER2, with an IC50 of 14 nM. ESCC cell lines are sensitive to Afatinib, and the IC50s are at a lower micro-molar range. Afatinib can strongly induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in HKESC-2 and EC-1.
In summary, Afatinib is an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor and has the potential for research of ESCC and NSCLC cancer.
Reference:
Li D, et al. Oncogene. 2008 Aug 7;27(34):4702-11.; Wong CH, et al. Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;5(12):3588-99.