c-Met is the cellular receptor for the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Activation of the HGF⁄c-Met pathway always leads to tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important molecule in tumor progression. Additionally, VEGF is associated with tumor angiogenesis. Due to their important role in tumor progression, they attractive targets for therapeutic intervention in cancer
In this article, we will introduce a potent c-Met and VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor, Golvatinib.
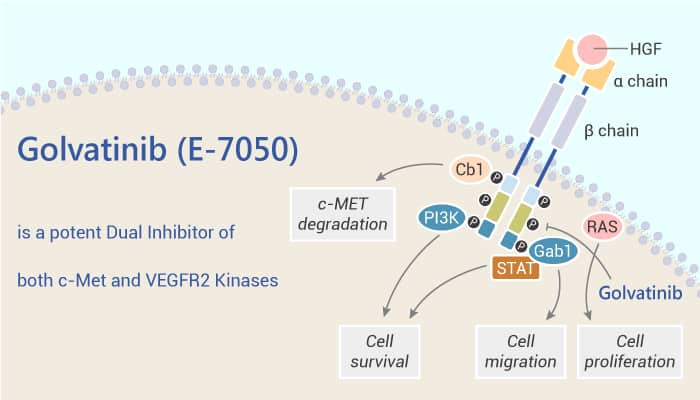
Golvatinib potently inhibits phosphorylation of both c-Met and VEGFR-2. The IC50 for c-Met and VEGFR2 kinases are and 16 nM, respectively. Additionally, Golvatinib also potently represses the growth of both c-met amplified tumor cells and endothelial cells stimulated with either HGF or VEGF.
In vitro, Golvatinib strongly inhibits the growth of MKN45, EBC-1, Hs746T, and SNU-5 tumor cells. And the IC50 values are 37, 6.2, 23, and 24 nM for these cell lines, respectively. Furthermore, Golvatinib also inhibits the growth of A549, SNU-1, and 0MKN74 tumor cells. But the IC50 values are much higher.
In EGFR mutant lung cancer cell lines, Golvatinib blocks the Met/Gab1/PI3K/Akt pathway in vitro. Thereby, Golvatinib circumvents resistance to all of the reversible, irreversible, and mutant-selective EGFR-TKIs induced by exogenous and/or endogenous HGF.
in xenograft models, Golvatinib shows inhibition of the phosphorylation of c-Met and VEGFR-2 in tumors, And it also exhibits strong inhibition of tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis.
Treatment of some tumor lines containing c-met amplifications with high doses of Golvatinib (50-200 mg/kg) induced tumor regression and disappearance. Additionally, In a peritoneal dissemination model, Golvatinib shows an antitumor effect against peritoneal tumors. As well as significant prolongation of lifespan in treated mice. In a combination tumor-treatment model, Golvatinib plus Gefitinib results in marked regression of tumor growth. This associate with inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in cancer cells.
In conclusion, Golvatinib, as a potent c-Met/VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor, is usually used for cancer research.
Reference:
[1]. Nakagawa T et al. Cancer Sci, 2010, 101(1), 210-215.