NSCLC accounts for almost 85% of all lung cancers. Additionally, lung cancer continues to be the most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are key drivers of NSCLC malignancy. Patients with the most common EGFR mutations (L858R mutation in exon 21 and delE746-A750 deletions in exon 19) typically have good responses to therapy with first-generation reversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as erlotinib or gefitinib. Research suggests that T790M mediates resistance to first-generation EGFR inhibitors by acting as a “gatekeeper” mutation, inducing steric hindrance in the ATP-binding pocket and preventing inhibitor binding. Patients with mutant EGFR NSCLC who have failed treatment with first-generation EGFR TKIs and have acquired resistance through the T790M mutation have few treatment options. Rociletinib is an orally delivered kinase inhibitor that specifically targets the mutant forms of EGFR including T790M.
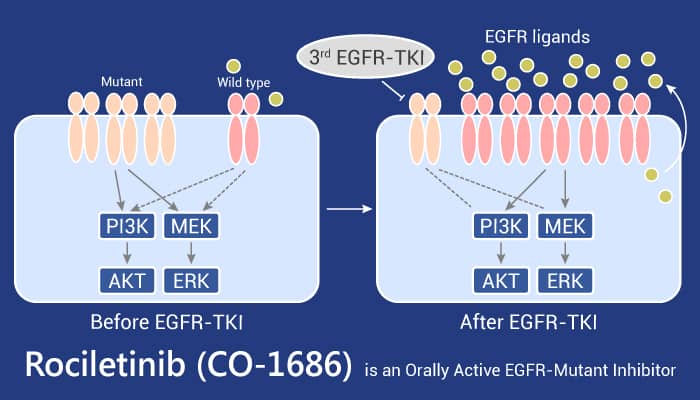
Rociletinib is a mutant-selective covalent inhibitor of EGFR that overcomes T790M-mediated resistance in NSCLC.
It is a potent inhibitor of EGFR L858R/T790M kinase. The Ki values for EGFRL858R/T790M and EGFRWT are 21.5 nM and 303.3 nM, respectively. Rociletinib is approximately 22-fold selective over WT EGFR. Rociletinib has a favorable selectivity profile when profiled against 434 kinases. In summary, Rociletinib is the first EGFR inhibitor in clinical development that is mutant-selective and inhibits T790M more potently than WT EGFR. Rociletinib potently and selectively inhibits the growth of NSCLC cells expressing mutant EGFR and induces apoptosis. Rociletinib resistant NSCLC cell lines are sensitive to AKT inhibition. It also demonstrates anti-tumor activity in NSCLC EGFR mutant xenograft models. Rociletinib (50 mg/kg bid, p.o.) demonstrates anti-tumor activity in human EGFR-L858R and EGFR-L858R-T790M expressing transgenic mice.
In summary, Rociletinib irreversibly and selectively inhibits mutant EGFR, in particular the T790M drug-resistance mutation, in NSCLC models. Rociletinib is the first drug of its class in clinical development for the treatment of T790M-positive NSCLC, potentially offering potent inhibition of mutant EGFR while avoiding the on-target toxicity observed with inhibition of the WT EGFR.
Reference:
Walter AO, et al. Cancer Discov. 2013 Sep 25.