Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (abbreviated Btk or BTK) is a tyrosine kinase that is encoded by the BTK gene in humans. BTK, a kinase expressed in B cells and bone marrow cells, has a well-characterized important role in B cells, vital role in B cells highlighted by the human primary immune deficiency disease, X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), which results from mutation in the BTK gene. BTK plays an essential role in the BCR signaling pathway. Recent appreciation for the extent to which BTK drives select hematological malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has spurred the development of targeted BTK inhibitors.
ARQ 531 (also known as MK-1026) is a potent, ATP-competitive, reversible non-covalent and orally active Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibitor. In addition, ARQ 531 potently inhibits TEC family kinases including the target kinase BTK, and several Src family kinases. However, ARQ 531 does not interact with C481, suggesting that C481S mutation would not affect binding. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells, ARQ 531 inhibits BCR-mediated activation of BTK, AKT, and ERK in a dose-dependent manner. In particular, this compound also dephosphorylates both the Y551 and Y223 activation sites of BTK. Additionally, ARQ 531 decreases the viability of CLL cells in a dose-dependent manner. ARQ 531 abrogates CpG mediated activation and chemokine induced migration of CLL cells. In vivo, ARQ 531 can increases survival in a murine Eμ-TCL1 engraftment model of CLL and a murine Eμ-MYC/TCL1 engraftment model resembling Richter transformation.
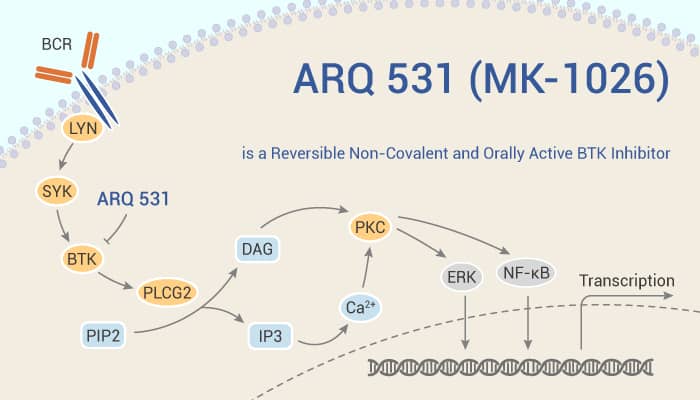
To sum up, ARQ 531 is a potent, ATP-competitive, reversible non-covalent and orally active BTK inhibitor, with anti-tumor activities.
References:
[1] Sean D Reiff, et al. Cancer Discov. 2018 Oct;8(10):1300-1315.